1. Krashen's Input Hypothesis (An Innatist Model)
(사진출처: 박현수 Build-up 영어교육론1)
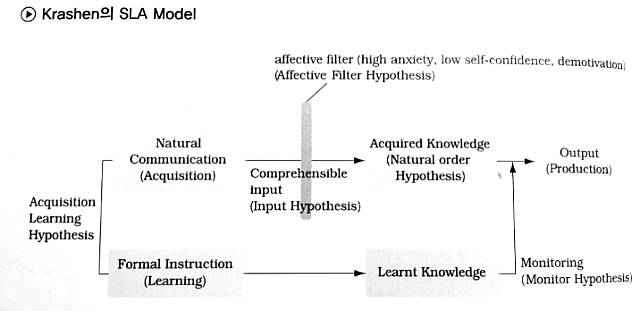
1) Acquisition-Learning Hypothesis
Acquisition: subconscious and intuitive process
natural, meaningful, real, authentic communication
focus on meaning
informal instruction
acquired knowledge
Learning: conscious process
form, grammar, rules
formal instruction
learnt knowledge
→ Non-interface position: "Acquired knowledge and learnt knowledge are entirely separate and unrelated."
2) Monitor Hypothesis
Monitor = Editor
using Learnt Knowledge
Form > Meaning
3) Natural Order Hypothesis
Grammar structures - predictable
independent of instructional sequences
4) Input Hypothesis
Comprehensible input (i+1)
Natural order
Silent period → speech will emerge
5) Affective filter Hypothesis
A mental block
Affective Variables: motivation, self-esteem, anxiety
2. Long's Interaction Hypothesis (A Social Constructivist Model)
Comprehensible Input + Corrective Feedback
by Modified Interaction & Negotiation of meaning
Input Modification - vocabulary, pronunciation, grammar,non-verbal
Interaction Modification - for negotiation of meaning & checking conversational flow
Comprehension checks
Clarification request
Confirmation checks
Repetition
Reformulation
Completion
3. Merril Swain’s Output Hypothesis
Pushed Output - to notice the gap between what learners want to say and what they are able to say
to try out new rules and modify them
to reflect on language itself in interaction
마지막으로, 위의 세 가설을 요약해보았습니다.
According to the Krashen’s Input Hypothesis, when students receive ‘comprehensible input,’ which is just beyond their current language ability, they acquire the knowledge of the language along the natural order. Although Long’s Interaction Hypothesis agrees with the importance of the comprehensible input, it further argues that ‘modified interaction’ during the conversation is a necessary condition for acquisition. That is, negotiation of meaning in the conversation makes input comprehensible. Finally, Swain, who states the Output Hypothesis, extends this argument that ‘pushed output’ is a significant factor for language acquisition as it helps the learners find the gap between what they can say and what they want to say. Therefore, it leads students to produce the target language more accurately and appropriately.
참고자료: PLLT 교재, 박현수 build-up 영어교육론1
![]() input, interaction, output.pptx
input, interaction, output.pptx