Spinal Cord
The spinal cord (Figure 04a) lies along the middorsal line of the body. It has two main functions: (1) it is the center for many reflex actions, and (2) it provides a means of commu-nication between the brain and the spinal nerves that leave the cord (Figure 04b). The white matter of the cord is white because it contains myelinated long fibers of interneurons that run to-gether in bundles call tracts. These tracts connect the cord to the brain. The dorsal ones are primarily ascending to the brain, while the ventral tracts bring information down from the brain. The inner portion of the
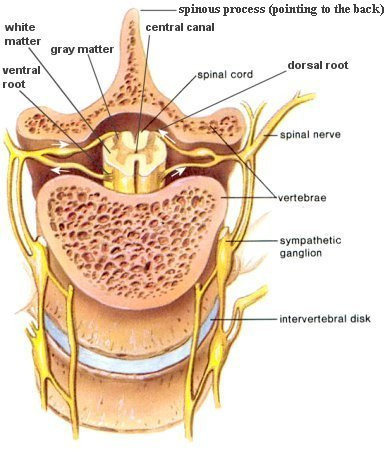
Figure 04a Spinal Cord
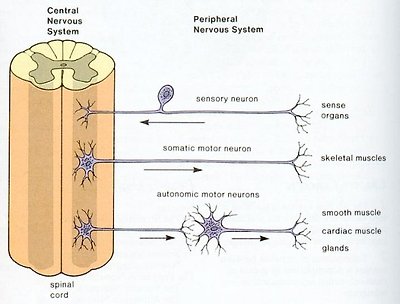
Figure 04b CNS and PNS
cord is filled with a mass of nerve cell bodies called gray matter. Each spinal nerve emerges from the spinal cord as two short branches, the dorsal and the ventral roots. These roots join just before the nerve leaves the vertebral column.
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system is outside the CNS. It consists of the various nerves that connect particular parts of the CNS with particular organs. Humans have 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Cranial nerves (Figure 05) are either sensory nerves, motor nerves, or mixed nerves. All of them, except the vagus nerve, control the head, the face, the neck, and the shoulders. The vagus nerve controls the internal organs. Table 04 lists the functions of the various cranial nerves. All spinal nerves (Figure 06) are mixed nerves that take impulses to and from the spinal cord. Table 05
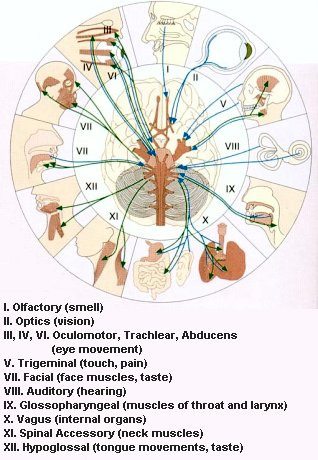
Figure 05 Cranial Nerves
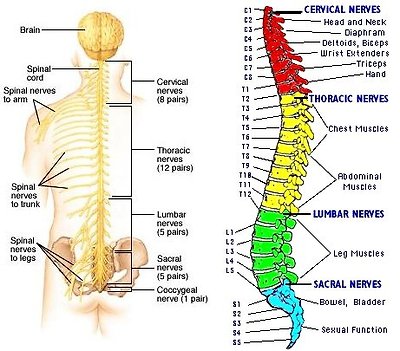
Figure 06 Spinal Nerves
describes the symptom of spinal cord injury (SCI) with the particular spinal nerve(s).
| Cranial Nerve | CN# | Brain Region | Major Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terminal§ | 0 | Near the olfactory | Reception of pheromone for sex |
| Olfactory | 1 | Cerebral Cortex | Smell |
| Optic | 2 | Limbic System | Vision |
| Oculomotor | 3 | Midbrain | Eyelid & eyeball movement; pupil dilation |
| Trochlear | 4 | Pons | Control downward & lateral eye movement |
| Trigeminal | 5 | " | Chewing; sensation of face & mouth |
| Abducens | 6 | " | Control lateral eye movement |
| Facial | 7 | " | Control most facial expressions; secretion of tears & saliva; taste; ear sensation |
| Auditory | 8 | Medulla | Hearing; balance |
| Glossopharyngeal | 9 | " | Taste; swallowing; sensation from tongue, tonsil, pharynx, carotid blood pressure |
| Vagus | 10 | " | Sensory, motor and autonomic functions of viscera - glands, digestion, heart rate, breathing rate, aortic blood pressure |
| Spinal Accessory | 11 | " | Controls muscles used in head movement |
| Hypoglossal | 12 | " | Controls tongue movements |
Table 04 Functions of Cranial Nerves
※The exact function of the terminal nerve in human is still under investigation, which is hampered by its small size and proximity to the olfactory nerve. For mouse and other animals at least, it is connected to the vomeronasal organ (vestige in human), which leads to a pathway for controlling sexual arousal.
| Spinal Nerve(s) | Innervated Body Part(s) | Symptom(s) of SCI |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | Head and Neck | Quadriplegia |
| C2-C4 | Diaphragm | Breathing problem |
| C5 | Deltoids, biceps | No control at wrist or hand |
| C6 | Wrist extenders | No hand function |
| C7-T1 | Triceps, hand | dexterity problems with hand and fingers |
| T2-T8 | Chest muscles | Paraplegia, poor trunk control |
| T9-T12 | Abdominal muscles | Paraplegia |
| Lumbar and Sacral | Leg muscles, bowel, bladder, sexual organs | Decreasing control of hip flexors and legs, dysfunction of bowel, bladder, and sex |
Table 05 Symptom(s) of Spinal Cord Injury
Note: Other effects of SCI may include low blood pressure, inability to regulate blood pressure effectively, reduced control of body temperature, inability to sweat below the level of injury, and chronic pain.
Autonomic Nervous System
One division of the autonomic nervous system, called the sympathetic nervous system, dominates in times of stress. It controls the "fight or flight" reaction, increasing blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, and blood flow to the muscles. Another division, called the parasympathetic nervous system, has the opposite effect. It conserves energy by slowing the heartbeat and breathing rate, and by promoting digestion and elimination (of waste). Most glands, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles constantly get inputs from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The CNS controls the activity by varying the ratio of the signals. Depending on which motor neurons are selected by the CNS, the net effect of the arriving signals
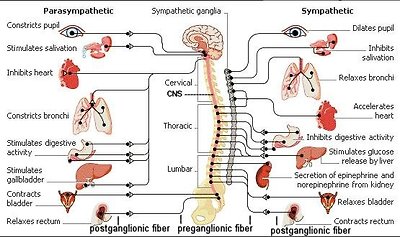
Figure 07 ANS Side View
will either stimulate or inhibit the organ. Figure 07 shows the various organs and actions, which are related to the two different divisions.
Motor fibers that govern involuntary responses, do not lead directly to the organs they innervate. Instead, they make their trips in two stages. The first set of fibers leads from the CNS to ganglia (which are collections of nerve cell bodies) that lie outside the CNS (the preganglionic fibers). At the ganglia the fibers form synaptic junctions with the dendrites of as many as twenty different cell bodies. The axons of these cell bodies form a second set of fibers, the postganglionic fibers. It is these postganglionic fibers that lead to the organs.
The chief ganglia involved in the autonomic nervous system form two lines running down either side of the spinal column. They are outside the bony vertebrae. These two lines of ganglia outside the column resemble a pair of long beaded cords. At the lower end, the two cords join and finish in a single central stretch. These lines of ganglia are sometimes called the sympathetic trunks (used by the sympathetic nervous system). Not all ganglia are located in the sympathetic trunks. Some are not; and it is possible for a preganglionic fiber to go right through, making no synaptic junction there at all, joining instead with ganglia located in front of the vertebrae. For the parasympathetic nervous system, some of the ganglia separating the preganglionic fibers from the postganglionic fibers are actually located within the organ the nerve is servicing. In that case, the preganglionic fiber runs almost the full length of the total track, whereas the postganglionic fiber is at most just a few millimeters long.
The splanchnic nerves, which originate from some of the thoracic nerves, have their preganglionic fibers ending in a mass of ganglia lying just behind the stomach. It represents the largest mass of nerve cells that is not within the CNS and is sometimes called the "abdominal brain". It is a vital spot to be protected during boxing.
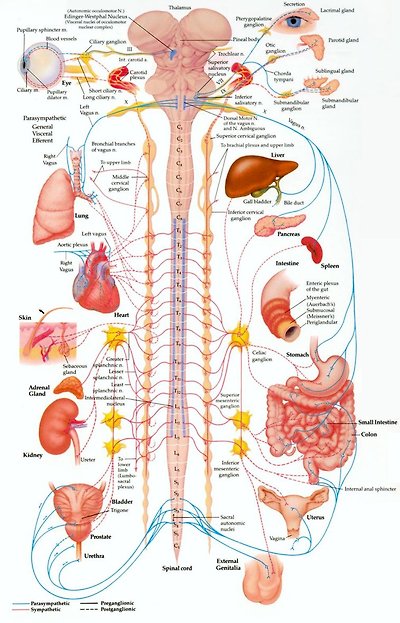
Figure 08 ANS Front View
Figure 08 is the front view of a more detailed ANS anatomy.
