3장. 최적화 기술
<= constraint를 만족하는 가장 작은 설계를 만든는 것
<= compile_ultra,compile
<= 타이밍과 면적 contraint간의 trade-off
① Optimizing for Delay
compile_ultra -auto_ungroup delay 로직을 자유롭게 변경
group_path
set_cost_priority –delay
compile_ultra -timing_effort_high_script 타이밍 개선 설정
② Optimizing for Area : 면적을 최소화
remove_constraint -all
set_max_area
compile -area_effort high option 혹은 -map_effort high
compile_ultra -area_effort_high_script
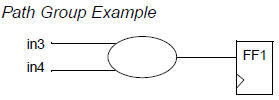
③ Creating Path Groups
<= 복작한 클락킹,타이밍,constraints이 요구시 path group을 만들거나 우선순위를 지정하여 최적화를 제어한다.
.경로 그룹 우선순위 : 0.0 ~ 100.0
group_path -name group3 -from in3 -to FF1/D -weight 2.5
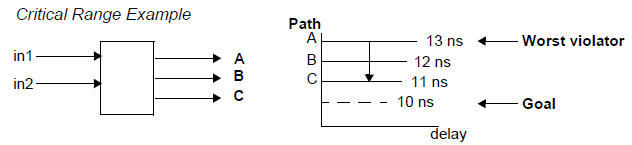
④ Optimizing Near-Critical Paths
경로 그룹에 임계범위를 추가하여, 최악의 음수 slack에서 임계 음수 slack
으로 최대 지연 비용 함수를 바꾼다.(임계 범위안에서 최적화됨)
실행시간이 길어지기 때문에 최종 구현 단계에서만 임계범위를 사용
최대 임계 범위 값은 클럭주기의 0.1값
Group_path –critical_range
Set_critical_range
create_clock -period 20 clk
set_critical_range 3.0 $current_design
set_max_delay 10 {A B C}
group_path -name group1 -to {A B C}
⑤ Fixing Heavily Loaded Nets
1) 방법
source constraints.con
compile_ultra
balance_buffer -from [get_pins buf1/Z]
2)방법
source constraints.con
compile_ultra
set_max_capacitance 3.0
compile -only_design_rule
⑥ Performing High-Effort Compile
dc_shell> elaborate my_design
dc_shell> compile -map_effort high
⑦ Performing a High-Effort Incremental Compile
dc_shell> dont_touch noncritical_blocks
dc_shell> compile -map_effort high -incremental_mapping
⑧ Disabling Total Negative Slack Optimization
dc_shell> set_max_area 0 -ignore_tns
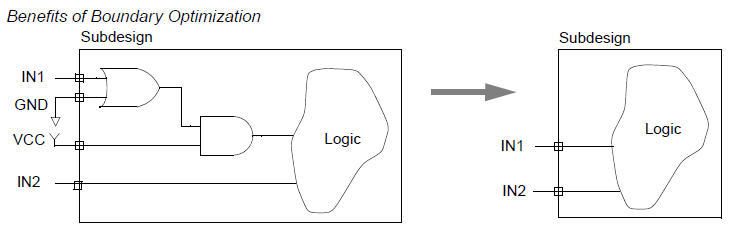
⑨ Optimizing Across Hierarchical Boundaries
dc_shell> compile_ultra
dc_shell> compile -boundary_optimization
dc_shell> set_boundary_optimization subdesign true | false
⑩ Propagating Constants
set_logic_one
set_logic_zero
set_unconnected
⑪ Enabling Critical Path Resynthesis
dc_shell> compile -map_effort high 임계 경로 재합성
⑫ Logic Duplication and Mapping to Wide-Fanin Gates
dc_shell> compile_ultra
dc_shell> compile –map_effort high
⑬ Removing Hierarchy
set_ungroup
ungroup
compile -ungroup_all
compile -auto_ungroup area
compile -auto_ungroup delay
compile_ultra
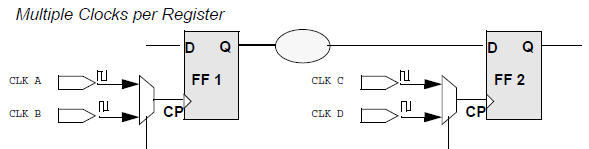
⑭ Optimizing for Multiple Clocks per Register
⑮ Optimizing Once for Best- and Worst-Case Conditions
Constraint-related commands
set_min_library
set_operating_conditions
set_wire_load_model
set_wire_load_mode
set_wire_load_min_block_size
set_wire_load_selection_group
set_clock_uncertainty
set_clock_transition
set_drive
set_load
set_port_fanout_number
set_resistance
Reporting commands
report_annotated_delay
report_area
report_attribute
report_bus
report_cache
report_cell
report_clock
report_clusters
report_compile_options
report_constraint
report_delay_calculation
report_design
report_design_lib
report_fpga
report_fsm
report_hierarchy
report_internal_loads
report_lib
report_name_rules
report_net
report_path_group
report_port
report_power
report_qor
report_reference
report_resources
report_synlib
report_timing
report_timing_requirements
report_transitive_fanin
report_transitive_fa
① Optimizing With Multiple Libraries
set_min_library
② Synthesizing to Multibit Components
Flip-flops
Latches
Master-slave circuits
Multiplexers
Three-state circuits
③ Buffering Nets Connected to Multiple Ports
④ Building a Balanced Buffer Tree
dc_shell> set_driving_cell -lib_cell IV io
dc_shell> balance_buffer -from io
dc_shell> balance_buffer -to {load1 load2}