제어판에서 내컴퓨터의 설정에서 확인하면 윈도우 버젼은 Windows 95 4.00.950b(Windows 95B OSR2.0)
으로 나오는데요
아래의 링크처럼 윈도우 인스톨러2,인터넷 익스플로어 5.5일본어버젼,usb 서플먼트를 설치하고 데몬3.47버젼을 설치했습니다만, 데몬으로 이미지를 마운트하고 탐색기를 열면 멈춥니다.(이미지는 오디오 트랙과 데이터 트랙이 혼합된 mixcd이미지입니다.)
http://blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=mattang_&logNo=110127436200
인터넷 익스플로어5.5일본어
http://oyasu.info/ie55/
usb 서플먼트
ftp://ftp.hp.com/ftp1/pub/softlib/software8/COL19186/jp-50156-1/vl7usb.exe
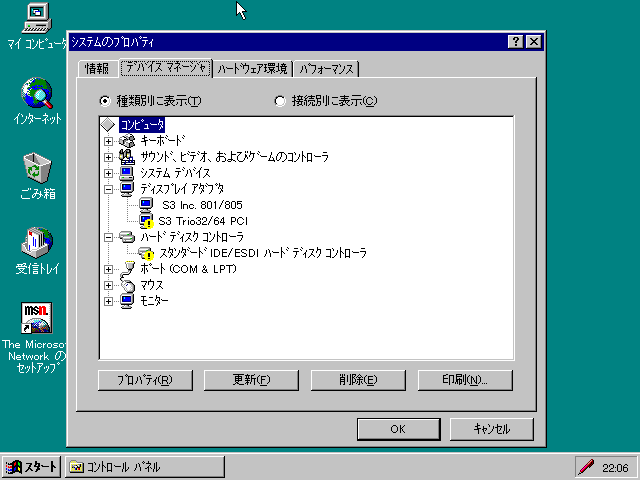
그리고 윈도우 95의 제어판의 시스템 설정에서 확인하면 하드디스크 controller탭과 디스플레이 아답터 탭의 standard IDE/ESDI하드 디스크 controller와 S3 Trio32/64 PCI에 문제가 있다고 나오는데 이 문제를 해결 할 수는 없나요?
dosbox버젼은 자료실에 등록된 SVN 특별버젼의 1월 27일자 최신버젼을 사용하고 있고 아래는 제 dosbox.conf의 설정인데 뭔가 잘못된 설정이 있나요?
windows95b에서 데몬툴 사용에 문제가 없으신분이 계시면 답변 좀 해주시면 좋겠습니다.
# This is the configuration file for DOSBox SVN-Daum. (Please use the latest version of DOSBox)
# Lines starting with a # are comment lines and are ignored by DOSBox.
# They are used to (briefly) document the effect of each option.
[sdl]
# fullscreen: Start dosbox directly in fullscreen. (Press ALT-Enter to go back)
# fulldouble: Use double buffering in fullscreen. It can reduce screen flickering, but it can also result in a slow DOSBox.
# fullresolution: What resolution to use for fullscreen: original, desktop or a fixed size (e.g. 1024x768).
# Using your monitor's native resolution with aspect=true might give the best results.
# If you end up with small window on a large screen, try an output different from surface.
# windowresolution: Scale the window to this size IF the output device supports hardware scaling.
# (output=surface does not!)
# output: What video system to use for output.
# Possible values: surface, overlay, opengl, openglnb, openglhq, ddraw, direct3d.
# autolock: Mouse will automatically lock, if you click on the screen. (Press CTRL-F10 to unlock)
# sensitivity: Mouse sensitivity.
# waitxxxxxxxxonerror: Wait before closing the console if dosbox has an error.
# priority: Priority levels for dosbox. Second entry behind the comma is for when dosbox is not focused/minimized.
# pause is only valid for the second entry.
# Possible values: lowest, lower, normal, higher, highest, pause.
# mapperfile: File used to load/save the key/event mappings from. Resetmapper only works with the default value.
# pixelshader: Pixelshader program (effect file must be in Shaders subdirectory). If 'forced' is appended,
# then the shader will be used even if the result might not be desired.
# usescancodes: Avoid usage of symkeys, might not work on all operating systems.
# overscan: Width of overscan border (0 to 10). (works only if output=surface)
fullscreen=false
fulldouble=false
fullresolution=desktop
windowresolution=original
output=direct3d
autolock=true
sensitivity=100
wait[안내]태그제한으로등록되지않습니다-xx[안내]태그제한으로등록되지않습니다-xx[안내]태그제한으로등록되지않습니다-xx[안내]태그제한으로등록되지않습니다-xxonerror=true
priority=higher,normal
mapperfile=mapper-SVN-Daum.map
pixelshader=none
usescancodes=false
overscan=0
[dosbox]
# language: Select another language file.
# machine: The type of machine DOSBox tries to emulate.
# Possible values: hercules, cga, cga_mono, tandy, pcjr, ega, vgaonly, svga_s3, svga_et3000, svga_et4000, svga_paradise, vesa_nolfb, vesa_oldvbe, amstrad.
# vmemsize: Amount of video memory in megabytes.
# The maximum resolution and color depth the svga_s3 will be able to display
# is determined by this value.
# 0: 512k (800x600 at 256 colors)
# 1: 1024x768 at 256 colors or 800x600 at 64k colors
# 2: 1600x1200 at 256 colors or 1024x768 at 64k colors or 640x480 at 16M colors
# 4: 1600x1200 at 64k colors or 1024x768 at 16M colors
# 8: up to 1600x1200 at 16M colors
# For build engine games, use more memory than in the list above so it can
# use triple buffering and thus won't flicker.
#
# captures: Directory where things like wave, midi, screenshot get captured.
# mainline compatible mapping: If set, arrange private areas, UMBs, and DOS kernel structures by default in the same way the mainline branch would do it.
# If cleared, these areas are allocated dynamically which may improve available memory and emulation accuracy.
# If your DOS game breaks under DOSBox-X but works with mainline DOSBox setting this option may help.
# adapter rom is ram: Map adapter ROM as RAM (mainline DOSBox 0.74 behavior). When clear, unused adapter ROM is mapped out
# private area size: Set DOSBox-X private memory area size. This area contains private memory structures used by the DOS kernel.
# It is discarded when you boot into another OS. Mainline DOSBox uses 32KB. Testing shows that it is possible
# to run DOSBox with as little as 4KB. If DOSBox-X aborts with error "not enough memory for internal tables"
# then you need to increase this value.
# memsize: Amount of memory DOSBox has in megabytes.
# This value is best left at its default to avoid problems with some games,
# though few games might require a higher value.
# There is generally no speed advantage when raising this value.
# memsizekb: Amount of memory DOSBox has in kilobytes.
# This value should normally be set to 0.
# If nonzero, overrides the memsize parameter.
# Finer grained control of total memory may be useful in
# emulating ancient DOS machines with less than 640KB of
# RAM or early 386 systems with odd extended memory sizes.
#
# memalias: Memory aliasing emulation, in number of valid address bits.
# . Many 386/486 class motherboards and processors prior to 1995
# suffered from memory aliasing for various technical reasons. If the software you are
# trying to run assumes aliasing, or otherwise plays cheap tricks with paging,
# enabling this option can help. Note that enabling this option can cause slight performance degredation. Set to 0 to disable.
# Recommended values when enabled:
# 24: 16MB aliasing. Common on 386SX systems (CPU had 24 external address bits)
# or 386DX and 486 systems where the CPU communicated directly with the ISA bus (A24-A31 tied off)
# 26: 64MB aliasing. Some 486s had only 26 external address bits, some motherboards tied off A26-A31
#
# vga bios size override: VGA BIOS size override. Override the size of the VGA BIOS (normally 32KB in compatible or 12KB in non-compatible).
# forcerate: Force the VGA framerate to a specific value(ntsc, pal, or specific hz), no matter what
# cgasnow: When machine=cga, determines whether or not to emulate CGA snow
# pit hack: If set, demo/game-specific hacks are applied to PIT timer emulation to help
# stabilize the demo and run more reliably. Valid values are:
# 'project_angel_demo' If you intend to run the Project Angel demo, use this
# setting. The PIT timer is forced to one of two values
# to resolve hangups, timing issues, music skipping on
# video mode changes, and VGA tearlines.
# 'pc_speaker_as_timer' A few early DOS demos apparently like to use PIT 2 as
# a timer source (where normally PIT 2 is used to generate
# a square wave to drive the PC speaker). If the demo you
# are running seems to run at half the normal speed for no
# logical reason, try this hack. Demos that need this hack:
# - Impact Studios, Legend
# Possible values: , project_angel_demo, pc_speaker_as_timer.
language=
machine=svga_s3
vmemsize=4
captures=capture
mainline compatible mapping=true
adapter rom is ram=false
private area size=32768
memsize=16
memsizekb=0
memalias=0
vga bios size override=0
forcerate=
cgasnow=true
pit hack=
[render]
# frameskip: How many frames DOSBox skips before drawing one.
# aspect: Do aspect correction, if your output method doesn't support scaling this can slow things down!.
# linewise: Draw the display line by line. Needed for certain special graphics effects in games and demos. Can be changed at runtime but will be put in effect at the next mode switch.
# char9: Allow 9-pixel wide text mode fonts.
# doublescan: If set, doublescanned output emits two scanlines for each source line, in the
# same manner as the actual VGA output (320x200 is rendered as 640x400 for example).
# If clear, doublescanned output is rendered at the native source resolution (320x200 as 320x200).
# This affects the raster PRIOR to the software or hardware scalers. Choose wisely.
#
# scaler: Scaler used to enlarge/enhance low resolution modes. If 'forced' is appended,
# then the scaler will be used even if the result might not be desired.
# Possible values: none, normal2x, normal3x, normal4x, normal5x, advmame2x, advmame3x, advinterp2x, advinterp3x, hq2x, hq3x, 2xsai, super2xsai, supereagle, tv2x, tv3x, rgb2x, rgb3x, scan2x, scan3x, hardware_none, hardware2x, hardware3x, hardware4x, hardware5x, xbrz.
# autofit: Best fits image to window
# - Intended for output=direct3d, fullresolution=original, aspect=true
frameskip=0
aspect=false
linewise=false
char9=false
doublescan=true
scaler=hardware2x
autofit=true
[vsync]
# vsyncmode: Synchronize vsync timing to the host display. Requires calibration within dosbox.
# Possible values: off, on, force, host.
# vsyncrate: Vsync rate used if vsync is enabled. Ignored if vsyncmode is set to host (win32).
# Possible values:.
vsyncmode=off
vsyncrate=75
[cpu]
# core: CPU Core used in emulation. auto will switch to dynamic if available and
# appropriate.
# Possible values: auto, dynamic, normal, full, simple.
# cputype: CPU Type used in emulation. auto emulates a 486 which tolerates Pentium instructions.
# Possible values: auto, 386, 486, pentium, 386_prefetch, pentium_mmx.
# cycles: Amount of instructions DOSBox tries to emulate each millisecond.
# Setting this value too high results in sound dropouts and lags.
# Cycles can be set in 3 ways:
# 'auto' tries to guess what a game needs.
# It usually works, but can fail for certain games.
# 'fixed #number' will set a fixed amount of cycles. This is what you usually
# need if 'auto' fails (Example: fixed 4000).
# 'max' will allocate as much cycles as your computer is able to
# handle.
# Possible values: auto, fixed, max.
# cycleup: Amount of cycles to decrease/increase with keycombos.(CTRL-F11/CTRL-F12)
# cycledown: Setting it lower than 100 will be a percentage.
# ignore opcode 63: When debugging, do not report illegal opcode 0x63.
# Enable this option to ignore spurious errors while debugging from within Windows 3.1/9x/ME
# apmbios: Emulate Advanced Power Management BIOS calls.
# Do not enable if you are running Windows ME.
# isapnpbios: Emulate ISA Plug & Play BIOS. Enable if using DOSBox to run a PnP aware DOS program or if booting Windows 9x.
# Do not disable if Windows 9x is configured around PnP devices, you will likely confuse it.
# realbig16: Allow the B (big) bit in real mode. If set, allow the DOS program to set the B bit,
# then jump to realmode with B still set (aka Huge Unreal mode). Needed for Project Angel.
core=auto
cputype=auto
cycles=auto
cycleup=10
cycledown=20
ignore opcode 63=true
apmbios=false
isapnpbios=false
realbig16=false
[keyboard]
# aux: Enable emulation of the 8042 auxiliary port. PS/2 mouse emulation requires this to be enabled.
# You should enable this if you will be running Windows ME or any other OS that does not use the BIOS to receive mouse events.
# auxdevice: Type of PS/2 mouse attached to the AUX port
# Possible values: none, 2button, 3button, intellimouse, intellimouse45.
aux=false
auxdevice=intellimouse
[pci]
# voodoo: Enable VOODOO support.
# Possible values: false, software, opengl, auto.
voodoo=auto
[mixer]
# nosound: Enable silent mode, sound is still emulated though.
# swapstereo: Swaps the left and right stereo channels.
# rate: Mixer sample rate, setting any device's rate higher than this will probably lower their sound quality.
# Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
# blocksize: Mixer block size, larger blocks might help sound stuttering but sound will also be more lagged.
# Possible values: 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 512, 256.
# prebuffer: How many milliseconds of data to keep on top of the blocksize.
nosound=false
swapstereo=false
rate=44100
blocksize=1024
prebuffer=20
[midi]
# mpu401: Type of MPU-401 to emulate.
# Possible values: intelligent, uart, none.
# mididevice: Device that will receive the MIDI data from MPU-401.
# Possible values: default, win32, alsa, oss, coreaudio, coremidi, mt32, synth, timidity, none.
# midiconfig: Special configuration options for the device driver. This is usually the id of the device you want to use.
# or in the case of coreaudio, you can specify a soundfont here.
# When using a Roland MT-32 rev. 0 as midi output device, some games may require a delay in order to prevent 'buffer overflow' issues.
# In that case, add 'delaysysex', for example: midiconfig=2 delaysysex
# See the README/Manual for more details.
# mt32.reverse.stereo: Reverse stereo channels for MT-32 output
# Possible values: off, on.
# mt32.verbose: MT-32 debug logging
# Possible values: off, on.
# mt32.thread: MT-32 rendering in separate thread
# Possible values: off, on.
# mt32.dac: MT-32 DAC input emulation mode
# Nice = 0 - default
# Produces samples at double the volume, without tricks.
# Higher quality than the real devices
#
# Pure = 1
# Produces samples that exactly match the bits output from the emulated LA32.
# Nicer overdrive characteristics than the DAC hacks (it simply clips samples within range)
# Much less likely to overdrive than any other mode.
# Half the volume of any of the other modes, meaning its volume relative to the reverb
# output when mixed together directly will sound wrong. So, reverb level must be lowered.
# Perfect for developers while debugging :)
#
# GENERATION1 = 2
# Re-orders the LA32 output bits as in early generation MT-32s (according to Wikipedia).
# Bit order at DAC (where each number represents the original LA32 output bit number, and XX means the bit is always low):
# 15 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 XX
#
# GENERATION2 = 3
# Re-orders the LA32 output bits as in later geneerations (personally confirmed on my CM-32L - KG).
# Bit order at DAC (where each number represents the original LA32 output bit number):
# 15 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 14
#
# Possible values: 0, 1, 2, 3, auto.
# mt32.reverb.mode: MT-32 reverb mode
# Possible values: 0, 1, 2, 3, auto.
# mt32.reverb.time: MT-32 reverb decaying time
# Possible values: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
# mt32.reverb.level: MT-32 reverb level
# Possible values: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
# mt32.partials: MT-32 max partials allowed (0-256)
mpu401=intelligent
mididevice=default
midiconfig=
mt32.reverse.stereo=off
mt32.verbose=off
mt32.thread=off
mt32.dac=auto
mt32.reverb.mode=auto
mt32.reverb.time=5
mt32.reverb.level=3
mt32.partials=32
[sblaster]
# sbtype: Type of Soundblaster to emulate. gb is Gameblaster.
# Possible values: sb1, sb2, sbpro1, sbpro2, sb16, sb16vibra, gb, none.
# sbbase: The IO address of the soundblaster.
# Possible values: 220, 240, 260, 280, 2a0, 2c0, 2e0, 300.
# irq: The IRQ number of the soundblaster.
# Possible values: 7, 5, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12.
# dma: The DMA number of the soundblaster.
# Possible values: 1, 5, 0, 3, 6, 7.
# hdma: The High DMA number of the soundblaster.
# Possible values: 1, 5, 0, 3, 6, 7.
# sbmixer: Allow the soundblaster mixer to modify the DOSBox mixer.
# oplmode: Type of OPL emulation. On 'auto' the mode is determined by sblaster type.
# All OPL modes are Adlib-compatible, except for 'cms'. sbtype=none
# together with oplmode=cms will emulate a Gameblaster.
# Possible values: auto, cms, opl2, dualopl2, opl3, none, hardware, hardwaregb.
# oplemu: Provider for the OPL emulation. compat might provide better quality (see oplrate as well).
# Possible values: default, compat, fast.
# oplrate: Sample rate of OPL music emulation. Use 49716 for highest quality (set the mixer rate accordingly).
# Possible values: 44100, 49716, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000.
# hardwarebase: base address of the real hardware soundblaster:
# 210,220,230,240,250,260,280
# goldplay: Enable goldplay emulation.
sbtype=sb16
sbbase=220
irq=7
dma=1
hdma=5
sbmixer=true
oplmode=auto
oplemu=default
oplrate=44100
hardwarebase=220
goldplay=false
[gus]
# gus: Enable the Gravis Ultrasound emulation.
# gusrate: Sample rate of Ultrasound emulation.
# Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
# gusbase: The IO base address of the Gravis Ultrasound.
# Possible values: 240, 220, 260, 280, 2a0, 2c0, 2e0, 300.
# gusirq: The IRQ number of the Gravis Ultrasound.
# Possible values: 5, 3, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12.
# gusdma: The DMA channel of the Gravis Ultrasound.
# Possible values: 3, 0, 1, 5, 6, 7.
# ultradir: Path to Ultrasound directory. In this directory
# there should be a MIDI directory that contains
# the patch files for GUS playback. Patch sets used
# with Timidity should work fine.
gus=false
gusrate=44100
gusbase=240
gusirq=5
gusdma=3
ultradir=C:\ULTRASND
[innova]
# innova: Enable the Innovation SSI-2001 emulation.
# samplerate: Sample rate of Innovation SSI-2001 emulation
# Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
# sidbase: SID base port (typically 280h).
# Possible values: 240, 220, 260, 280, 2a0, 2c0, 2e0, 300.
# quality: Set SID emulation quality level (0 to 3).
# Possible values: 0, 1, 2, 3.
innova=false
samplerate=22050
sidbase=280
quality=0
[speaker]
# pcspeaker: Enable PC-Speaker emulation.
# pcrate: Sample rate of the PC-Speaker sound generation.
# Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
# tandy: Enable Tandy Sound System emulation. For 'auto', emulation is present only if machine is set to 'tandy'.
# Possible values: auto, on, off.
# tandyrate: Sample rate of the Tandy 3-Voice generation.
# Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
# disney: Enable Disney Sound Source emulation. (Covox Voice Master and Speech Thing compatible).
# ps1audio: Enable PS1 audio emulation.
# Possible values: on, off.
# ps1audiorate: Sample rate of the PS1 audio emulation.
# Possible values: 44100, 48000, 32000, 22050, 16000, 11025, 8000, 49716.
pcspeaker=true
pcrate=44100
tandy=auto
tandyrate=44100
disney=false
ps1audio=off
ps1audiorate=22050
[joystick]
# joysticktype: Type of joystick to emulate: auto (default), none,
# 2axis (supports two joysticks),
# 4axis (supports one joystick, first joystick used),
# 4axis_2 (supports one joystick, second joystick used),
# fcs (Thrustmaster), ch (CH Flightstick).
# none disables joystick emulation.
# auto chooses emulation depending on real joystick(s).
# (Remember to reset dosbox's mapperfile if you saved it earlier)
# Possible values: auto, 2axis, 4axis, 4axis_2, fcs, ch, none.
# timed: enable timed intervals for axis. Experiment with this option, if your joystick drifts (away).
# autofire: continuously fires as long as you keep the button pressed.
# swap34: swap the 3rd and the 4th axis. can be useful for certain joysticks.
# buttonwrap: enable button wrapping at the number of emulated buttons.
joysticktype=auto
timed=true
autofire=false
swap34=false
buttonwrap=false
[serial]
# serial1: set type of device connected to com port.
# Can be disabled, dummy, modem, nullmodem, directserial.
# Additional parameters must be in the same line in the form of
# parameter:value. Parameter for all types is irq (optional).
# for directserial: realport (required), rxdelay (optional).
# (realport:COM1 realport:ttyS0).
# for modem: listenport (optional).
# for nullmodem: server, rxdelay, txdelay, telnet, usedtr,
# transparent, port, inhsocket (all optional).
# Example: serial1=modem listenport:5000
# Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, serialmouse, directserial.
# serial2: see serial1
# Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, serialmouse, directserial.
# serial3: see serial1
# Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, serialmouse, directserial.
# serial4: see serial1
# Possible values: dummy, disabled, modem, nullmodem, serialmouse, directserial.
serial1=dummy
serial2=dummy
serial3=disabled
serial4=disabled
[printer]
# printer: Enable printer emulation.
# dpi: Resolution of printer (default 360).
# width: Width of paper in 1/10 inch (default 85 = 8.5'').
# height: Height of paper in 1/10 inch (default 110 = 11.0'').
# printoutput: Output method for finished pages:
# png : Creates PNG images (default)
# ps : Creates Postscript
# bmp : Creates BMP images (very huge files, not recommend)
# printer : Send to an actual printer (Print dialog will appear)
# multipage: Adds all pages to one Postscript file or printer job until CTRL-F2 is pressed.
# docpath: The path where the output files are stored.
# timeout: (in milliseconds) if nonzero: the time the page will
# be ejected automatically after when no more data
# arrives at the printer.
printer=true
dpi=360
width=85
height=110
printoutput=png
multipage=false
docpath=.
timeout=0
[parallel]
# parallel1: parallel1-3 -- set type of device connected to lpt port.
# Can be:
# reallpt (direct parallel port passthrough),
# file (records data to a file or passes it to a device),
# printer (virtual dot-matrix printer, see [printer] section)
# Additional parameters must be in the same line in the form of
# parameter:value.
# for reallpt:
# Windows:
# realbase (the base address of your real parallel port).
# Default: 378
# ecpbase (base address of the ECP registers, optional).
# Linux: realport (the parallel port device i.e. /dev/parport0).
# for file:
# dev:<devname> (i.e. dev:lpt1) to forward data to a device,
# or append:<file> appends data to the specified file.
# Without the above parameters data is written to files in the capture dir.
# Additional parameters: timeout:<milliseconds> = how long to wait before
# closing the file on inactivity (default:500), addFF to add a formfeed when
# closing, addLF to add a linefeed if the app doesn't, cp:<codepage number>
# to perform codepage translation, i.e. cp:437
# for printer:
# printer still has it's own configuration section above.
# parallel2: see parallel1
# parallel3: see parallel1
# dongle: Enable dongle
parallel1=disabled
parallel2=disabled
parallel3=disabled
dongle=false
[glide]
# glide: Enable glide emulation: true,false,emu.
# lfb: LFB access: full,full_noaux,read,read_noaux,write,write_noaux,none.
# OpenGlide does not support locking aux buffer, please use _noaux modes.
# splash: Show 3dfx splash screen (requires 3dfxSpl2.dll).
glide=true
lfb=full
splash=true
[dos]
# xms: Enable XMS support.
# ems: Enable EMS support. The default (=true) provides the best
# compatibility but certain applications may run better with
# other choices, or require EMS support to be disabled (=false)
# to work at all.
# Possible values: true, emsboard, emm386, false.
# umb: Enable UMB support.
# umb start: UMB region starting segment
# umb end: UMB region last segment
# dynamic kernel allocation: If set, DOS kernel structures are allocated dynamically. If clear, DOS kernel structures are fixed at specific segments (mainline DOSBox behavior)
# keep umb on boot: If emulating UMBs, keep the UMB around after boot (Mainline DOSBox behavior). If clear, UMB is unmapped when you boot an operating system.
# keep private area on boot: If set, keep the DOSBox private area around after boot (Mainline DOSBox behavior). If clear, unmap and discard the private area when you boot an operating system.
# private area in umb: If set, keep private DOS segment in upper memory block, usually segment 0xC800 (Mainline DOSBox behavior)
# If clear, place private DOS segment at the base of system memory (just below the MCB)
# automount: Enable automatic mount.
# int33: Enable INT 33H (mouse) support.
# biosps2: Emulate BIOS INT 15h PS/2 mouse services
# Note that some OS's like Microsoft Windows neither use INT 33h nor
# probe the AUX port directly and depend on this BIOS interface exclusively
# for PS/2 mouse support. In other cases there is no harm in leaving this enabled
# keyboardlayout: Language code of the keyboard layout (or none).
# dbcs: Enable DBCS table
# filenamechar: Enable filename char table
# collating and uppercase: Enable collating and uppercase table
# files: Number of file handles available to DOS programs. (equivalent to "files=" in config.sys)
xms=true
ems=true
umb=true
umb start=0
umb end=0
dynamic kernel allocation=false
keep umb on boot=false
keep private area on boot=false
private area in umb=true
automount=true
int33=true
biosps2=true
keyboardlayout=auto
dbcs=true
filenamechar=true
collating and uppercase=true
files=127
[ipx]
# ipx: Enable ipx over UDP/IP emulation.
ipx=false
[ne2000]
# ne2000: Enable Ethernet passthrough. Requires [Win]Pcap.
# nicbase: The base address of the NE2000 board.
# nicirq: The interrupt it uses. Note serial2 uses IRQ3 as default.
# macaddr: The physical address the emulator will use on your network.
# If you have multiple DOSBoxes running on your network,
# this has to be changed for each. AC:DE:48 is an address range reserved for
# private use, so modify the last three number blocks.
# I.e. AC:DE:48:88:99:AB.
# realnic: Specifies which of your network interfaces is used.
# Write 'list' here to see the list of devices in the
# Status Window. Then make your choice and put either the
# interface number (2 or something) or a part of your adapters
# name, e.g. VIA here.
ne2000=true
nicbase=300
nicirq=3
macaddr=AC:DE:48:88:99:AA
realnic=list
[ide, primary]
# enable: Enable IDE interface
# int13fakeio: If set, force IDE state change on certain INT 13h commands.
# IDE registers will be changed as if BIOS had carried out the action.
# If you are running Windows 3.11 or Windows 3.11 Windows for Workgroups
# you must enable this option (and use -reservecyl 1) if you want 32-bit
# disk access to work correctly in DOSBox.
# int13fakev86io: If set, and int13fakeio is set, certain INT 13h commands will
# cause IDE emulation to issue fake CPU I/O traps (GPF) in
# virtual 8086 mode and a fake IRQ signal. you must enable this option
# if you want 32-bit disk access in Windows 95 to work with DOSBox.
enable=true
int13fakeio=false
int13fakev86io=false
[ide, secondary]
enable=true
int13fakeio=false
int13fakev86io=false
[ide, tertiary]
enable=true
int13fakeio=false
int13fakev86io=false
[ide, quaternary]
enable=true
int13fakeio=false
int13fakev86io=false
[autoexec]
# Lines in this section will be run at startup.
# You can put your MOUNT lines here.
[autoexec]
# Lines in this section will be run at startup.
# You can put your MOUNT lines here.
댓글
댓글 리스트-
작성자DOSBox─X 작성시간 14.01.30 데몬에서의 이미지 로드 사용은 원래부터 불안정했습니다. 도스박스 안에서도 직접 MP3 트랙의 이미지 로드가 가능한데 시도해 보셨나요?
-
작성자oldgmr 작성자 본인 여부 작성자 작성시간 14.01.31 역시 데몬은 윈도우95 에물레이션에서는 불안정하군요.원래 DOSBOX.conf의 [AUTOEXEC] imgmount d "d:\dosbox\uncharted water2.cue" -t iso 명령어로 이미지의 인식은 됩니다만 오디오 트랙의 재생이 실제 cue의 인덱스와 약간씩 다른것 같아서 데몬툴을 직접 설치해서 데몬툴에 마운트된 인덱싱과 비교하려고 했는데 아무래도 데몬툴을 직접 윈도우95에 인스톨하는 것은 힘들겠군요....
-
작성자DOSBox─X 작성시간 14.01.31 도스박스 자체에서 오디오 트랙을 포함한 ISO 이미지 지원은 이제서야 지원한 기능이라 일부 부족한 부분이 있을 수 있습니다.
-
작성자oldgmr 작성자 본인 여부 작성자 작성시간 14.02.01 결국 virtual pc 2007에서 win95를 인스톨해서 플레이하고 있습니다.버츄얼 pc의 win95의 믹스모드 시디의 오디오 트랙 재생과 dosbox의 win95에서의 오디오 트랙재생을 비교하면 아무래도 2번째 오디오 트랙 이후로 1~2초정도씩 재생에 차이가 나는 것 같습니다.
-
작성자DOSBox─X 작성시간 14.02.01 도움이 될만한 정보일 것으로 보여 말씀 드립니다. MP3가 아닌 OGG를 사용한다면 재생에 문제가 없음을 확인했습니다.