영어로 배우는 중학교 수학 - 다항식의 덧셈과 뺄셈 [ 영문 ] - Addition & Subtraction of Polynomials
작성자CLARK작성시간09.11.29조회수977 목록 댓글 0
영어로 중학교 수학 - " 다항식의 덧셈과 뺄셈 " 부분을 배워봅시다.
================================================================
We first used polynomials but did not identify them as polynomials.
In Chapter 1 we defined a term as an expression containing a number or the product of a number and one or more variables raised to powers. Some examples of terms are
4x3, -x2y3 , 6ab , and -2.
A polynomial is a single term or a finite sum of terms. The powers of the variables in a polynomial must be positive integers. For example,
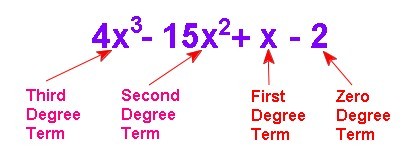
4x3 + (-15x2) + x + (-2)
Is a polynomial. Because it is simpler to write addition of a negative as subtraction, this polynomial is usually written as 4x3 – 15x2 + x – 2.
The degree of a polynomial in one variable is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. So 4x3 – 15x2 + x – 2 has degree 3 and 7w – w2 has degree 2.
The degree of a term is the power of the variable in the term. Because the last term has no variable, its degree is 0.
A single number is called a constant and so the last term is the constant term. The degree of a polynomial consisting of a single number such as 8 is 0.
The number preceding the variable in each term is called the coefficient of that variable or the coefficient of that term. In 4x3 – 15x2 + x – 2 the coefficient of x3 is 4, the coefficient of x2 is –15, and the coefficient of x is 1 because x = 1 × x.
E X A M P L E 1 Identifying coefficients
Determine the coefficients of x3 and x2 in each polynomial:
a) x3 + 5x2 – 6 b) 4x6 – x3 + x
Solution
a ) Write the polynomial as 1 × x3 + 5x2 – 6 to see that the coefficient of x3 is 1 and the coefficient of x2 is 5.
b) The x2-term is missing in 4x6 – x3 + x. Because 4x6 – x3 + x can be written as
4x6 – 1 × x3 + 0 × x2 + x,
the coefficient of x3 is – 1 and the coefficient of x2 is 0.
For simplicity we generally write polynomials with the exponents decreasing from left to right and the constant term last. So we write
x3 – 4x2 + 5x + 1 rather than -4x2 + 1 + 5x + x3.
When a polynomial is written with decreasing exponents, the coefficient of the first term is called the leading coefficient.
Certain polynomials are given special names. A monomial is a polynomial that has one term, a binomial is a polynomial that has two terms, and a trinomial is a polynomial that has three terms. For example, 3x5 is a monomial, 2x – 1 is a binomial, and 4x6 – 3x + 2 is a trinomial.
Identify each polynomial as a monomial, binomial, or trinomial and state its degree. a) 5x2 - 7x3 + 2 b) x43 – x2 c) 5x d) -12
Solution
Value of a Polynomial
A polynomial is an algebraic expression. Like other algebraic expressions involving variables, a polynomial has no specific value unless the variables are replaced by numbers. A polynomial can be evaluated with or without the function notation discussed in last Chapter.
E X A M P L E 3 Evaluating Polynomials
a) Find the value of – 3x4 – x3 + 20x + 3 when x = 1.
b) Find the value of – 3x4 – x3 +20x + 3 when x = – 2.
c) If P(x) = – 3x4 – x3 + 20x + 3, find P (1).
Solution a) Replace x by 1 in the polynomial:
–3x4 – x3 + 20x + 3 = – 3 (1)4 – (1)3 + 20(1) + 3
= – 3 – 1 + 20 + 3 = 19
b) Replace x by -2 in the polynomial:
–3x4 – x3 + 20x + 3 = – 3( – 2)4 – ( – 2)3 + 20( – 2) + 3
= – 3(16) – ( – 8) – 40 + 3
= –48 + 8 – 40 + 3 = – 77
So the value of the polynomial is – 77 when x = – 2.
c) This is a repeat of part (a) using the function notation from Chapter 2. P (1), read
“P of 1,” is the value of the polynomial P(x) when x is 1. To find P (1), replace x by
1 in the formula for P(x): P(x) = – 3x4 – x3 + 20x + 3
P(1) = – 3 (1)4 – (1)3 + 20(1) + 3 = 19
So P (1) = 19. The value of the polynomial when x = 1 is 19.
|