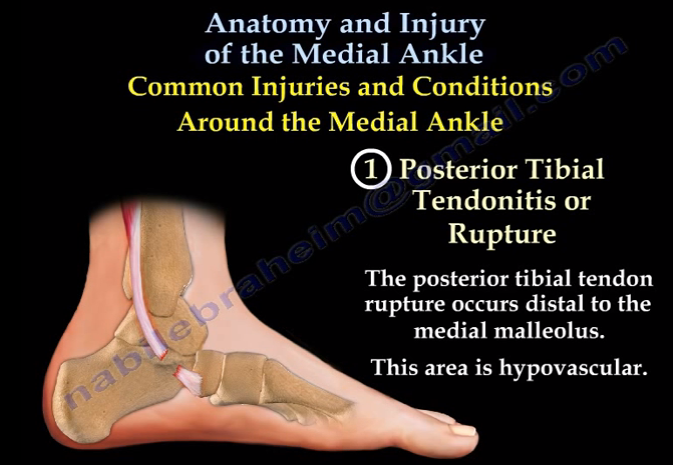
The blood supply of the posterior tibial tendon - 극상근, 아킬레스건과 같이 혈류공급이 좋지 않은 부위
작성자문형철작성시간13.12.24조회수950 목록 댓글 0아하..
후경골근건도 그렇구나..
We studied the vascular pattern of human posterior tibial tendons by injection techniques and immunohistochemically using antibodies against laminin. The intravascular volume of the posterior
tibial tendon was determined using a new method of injection of a solution of 99mTc and gelatin ink into
the lower legs of cadavers.
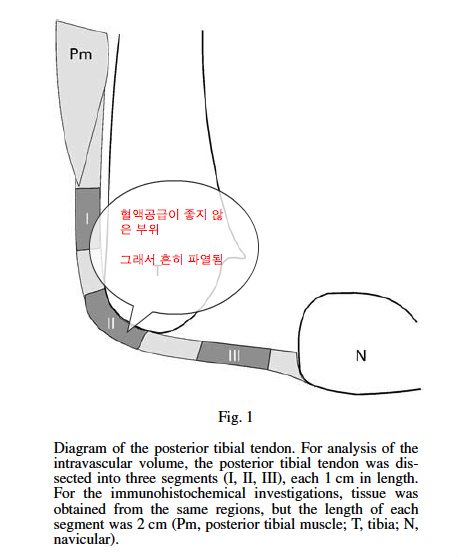
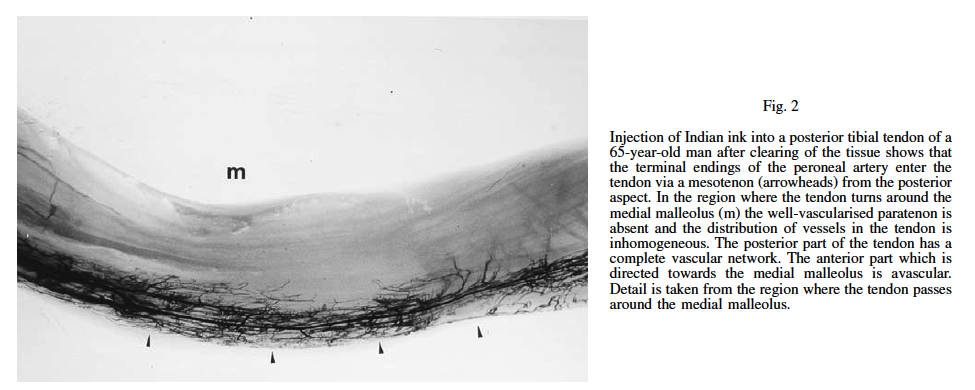
Three segments of 1 cm length from different regions of the human posterior tibial tendon were measured using a gamma well counter. The main blood supply arises from the posterior tibial artery. Blood vessels enter the paratenon of the posterior tibial tendon via a mesotenon from the posterior aspect. From the paratenon, the blood
vessels penetrate the posterior tibial tendon and anastomose with a longitudinally orientated intratendinous network. The number of vessels in the substance of the tendon is consistently less than that in the surrounding paratenon.
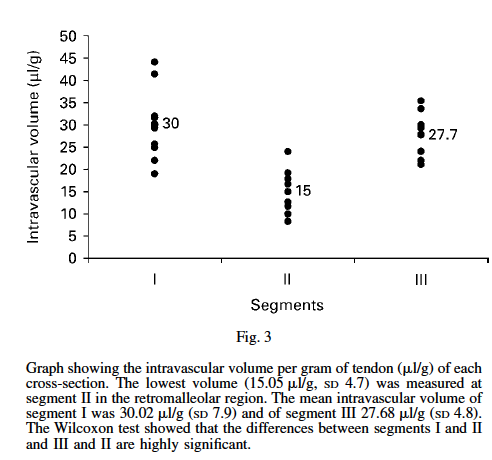
The distribution of blood vessels within the posterior tibial tendon is not homogeneous. In the retromalleolar region the intravascular volume was significantly reduced with a mean value of 15 l/g of tendon tissue. There was no significant difference between the mean intravascular volumes of the proximal and distal areas (distal,
27.7 l/g tendon tissue; proximal, 30 l/g tendon tissue). The immunohistochemical investigation showed that there was no immunostaining for laminin in the anterior part of the tendon in the region where it passes behind the medial malleolus. This region is avascular.
The most frequent site of rupture of the posterior tibial tendon is in the region behind the medial malleolus. A potential endogenous risk factor may be the limited healing potential of avascular tissue.
![]() posterior tibial tendon의 혈류공급에 대한 논문.pdf
posterior tibial tendon의 혈류공급에 대한 논문.pdf