초음파를 이용한 근육검사에 대한 논문
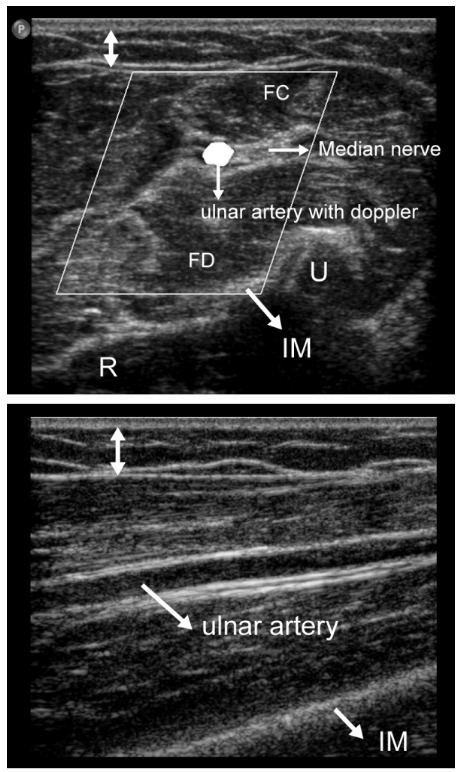
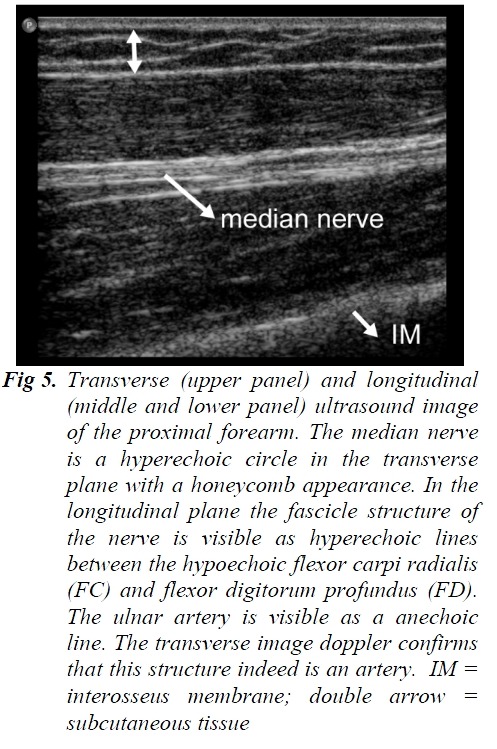
초음파 이미지의 기본은 bone, ligament, tendon, nerve, muscle, water 음영순으로 hypoecho
즉 물, 염증반응은 근골격계 초음파에서 검게 보인다.
![]() Skeletal muscle ultrasound.pdf
Skeletal muscle ultrasound.pdf
Abstract
Muscle ultrasound is a convenient technique to visualize normal and pathological muscle tissue as it is non-invasive and real-time. Neuromuscular disorders give rise to structural muscle changes that can be visualized with ultrasound:
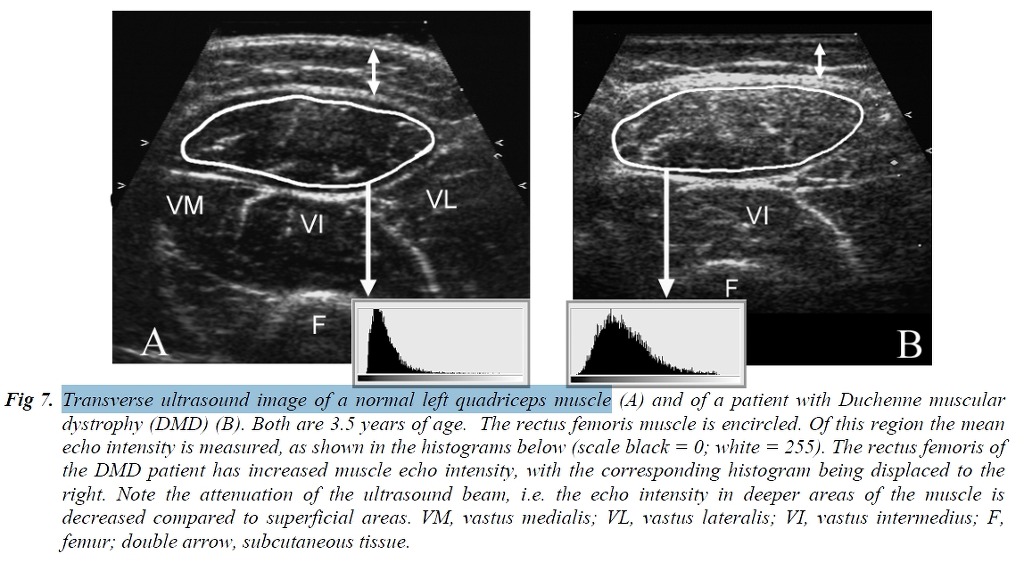
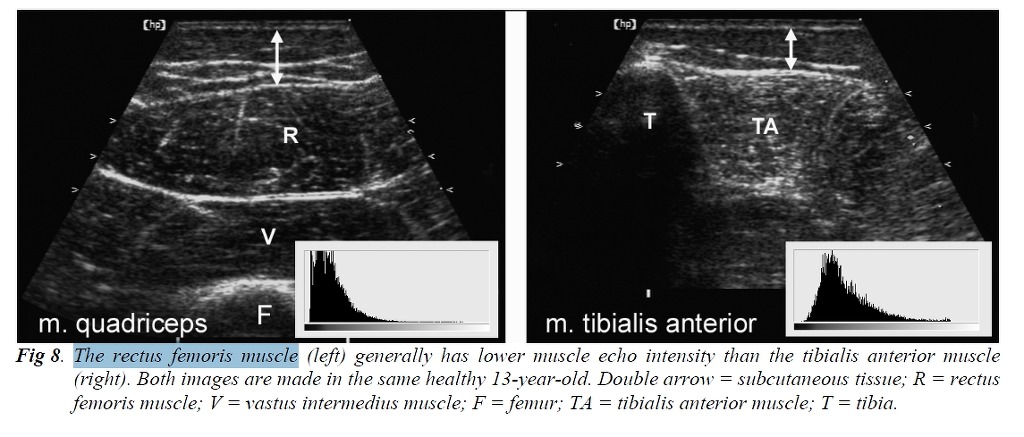
atrophy can be objectified by measuring muscle thickness, while infiltration of fat and fibrous tissue increase muscle echo intensity, i.e. the muscles become whiter on the ultrasound image. Muscle echo intensity need to be quantified to correct for age-related increase in echo intensity and differences between individual muscles. This can be done by gray scale analysis, a method that can be easily applied in daily clinical practice. Using this technique it is possible to detect neuromuscular disorders with predictive values of 90 percent.
Only in young children and metabolic myopathies the sensitivity is lower. Ultrasound is a dynamic technique and therefore capable of visualizing normal and pathological muscle movements. Fasciculations can easily be differentiated from other muscle movements. Ultrasound appeared to be even more sensitive in detecting fasciculations compared to EMG and clinical observations, because it can visualize a large muscle area and deeper located muscles. With improving resolution and frame rate it has recently become clear that also smaller scale spontaneous muscle activity such as fibrillations can be detected by ultrasound. This opens the way to a broader use of muscle ultrasound in the diagnosis of peripheral nerve and muscle disorders.
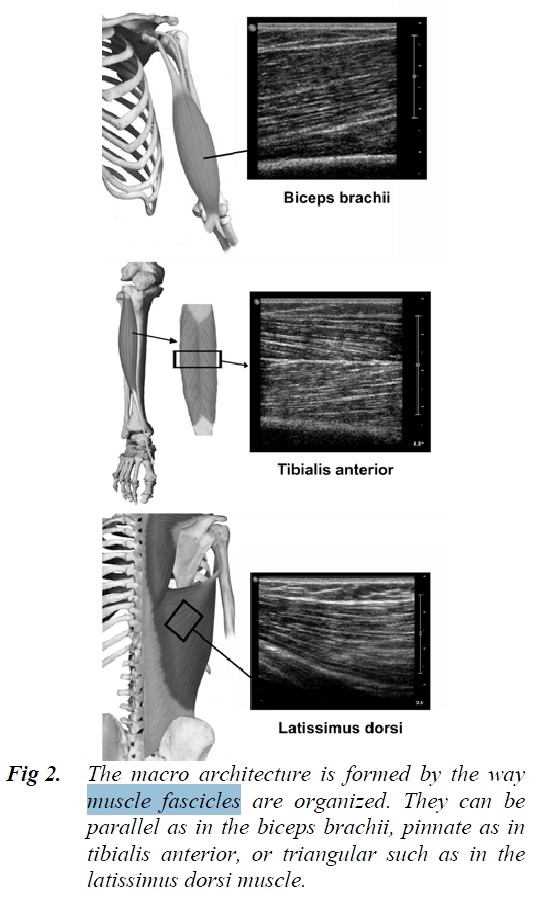
1. Ultrasound of normal muscle tissue
2. Muscle ultrasound in neuromuscular disorders
3. Diagnostic value of muscle ultrasound
4. Muscle ultrasound in specific neuromuscular disorders
5. Dynamic muscle ultrasound and the detection of fibrillations
6. Muscle ultrasound compared to other muscle imaging techniques
7. Future perspectives in muscle ultrasound
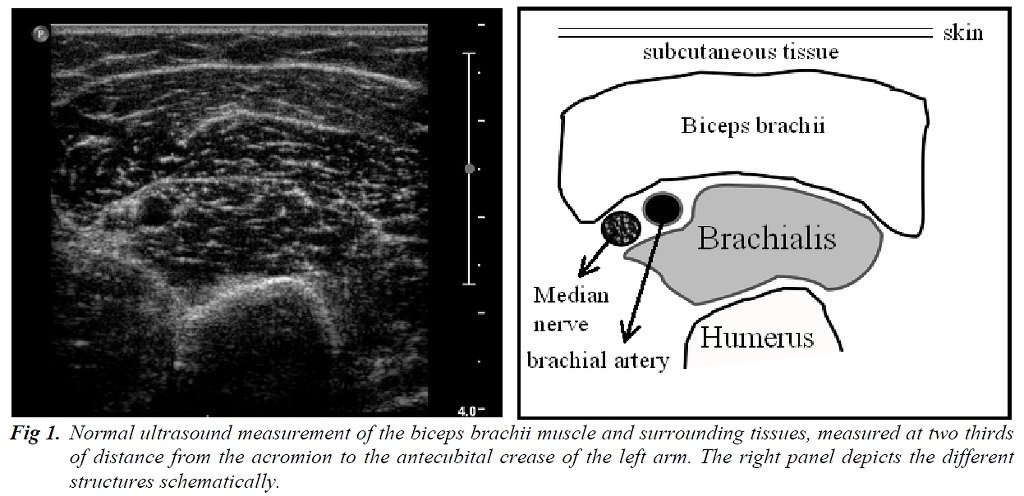
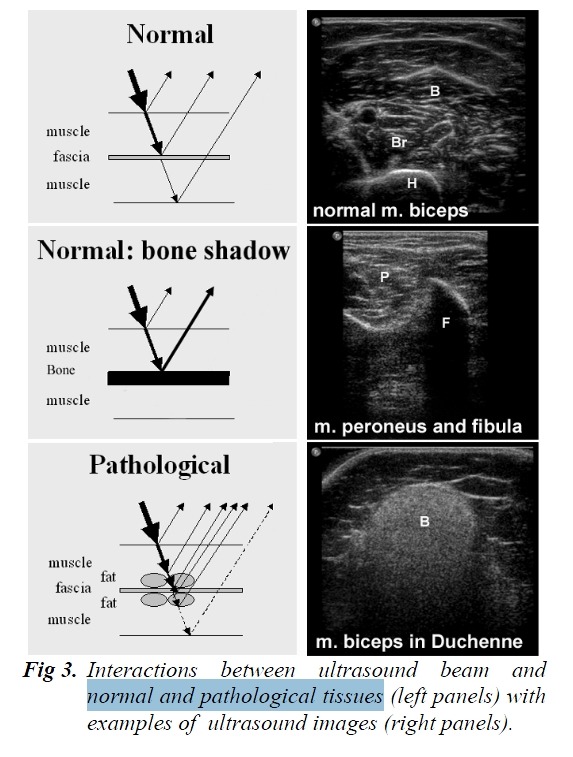
The boundaries of the muscle are clearly visible, as the epimysium surrounding the muscle is a highly
reflective structure. In normal subjects the bone echo is strong and distinct with an anechoic bone shadow
underneath (Fig 3).