궤양성대장염(크론병)의 자연치유, 미량원소 치유법 - 음식알레르기, 프로바이오틱스, 생선오일, 비타민 D9, 6, 12, C, D, 마그네슘, 철, DHEA, 멜라토닌, 커큐
작성자문형철작성시간19.10.03조회수6,196 목록 댓글 0beyond reason
미량원소 치유의학의 세계
궤양성 대장염은 6가지 영양물질이 부족해지므로 반드시 고려해야
- 칼륨
- 비타민 D
- 철분
- 비타민 B
- 포타슘
- 마그네슘
궤양성대장염(ulcerative colitis)
- 대장과 직장의 염증을 특징으로 하는 만성자가면역질병으로 복통, 설사, 직장출혈 등이 주요 증상
- 궤양성 대장염이라고 하면 대장에만 발생하는 염증으로 생각하기 쉬우나 관절, 척추(강직성 척추염), 피부, 눈(포도막염)에도 흔히 생김
- 궤양성대장염은 대장암으로 진행될 가능성이 높음
음식치료
1) 단백질, 칼로리, 영양소 등을 적절하게 보충해야 함.
2) 물을 충분히 마셔야
3) 음식알레르기를 찾아서 해결해야
음식알레르기
- 궤양성대장염 환자는 대장과 직장점막의 히스타민 수치가 증가하고 직장점막내 IgE가 포함된 세포수가늘어남.
- 궤양성대장염이 재발하는 경우 일부 환자에게서 순환 호산성백혈구(circulating eosinophil)의 수가 늘어나기 하는데 이런 현상도 알레르기를 의심할 수 있는 증거가 됨.
- 흔히 유제품, 밀, 달걀, 옥수수, 감귤류에 의한 알레르기가 흔함.
- 138명 궤양성대장염 환자의 원인 연구
- 45%가 음식 알레르기가 단독원인
- 3%는 꽃가루 알레르기가 단독원인
- 70%는 음식 알레르기와 연관되어 있음.
유당불내증(lactose intolerance)
- 우유의 유당을 분해하는 효소인 락타아제가 부족한 궤양성대장염 환자가 많게는 50%가 넘음
- 쉽게 표현하면 궤양성 대장염환자의 50%가 유제품을 먹지 않으면 증상이 호전됨
실리신산염 민감성(salicylate sensitivity)
- 살리신산염은 향신료(마늘, 생강, 후추, 강황, 계피)에 많이 함유되어 있음.
- 아몬드, 땅콩 등에 많음
- 아스피린의 주성분이므로 NSAIDs를 먹으면 악화됨.
자연치유제
1) 생선오일
- 생선오일에 함유된 오메가 3 지방산은 항염증 효능이 있어 궤양성대장염에 효과적
2) 엽산
- 궤양성대장염 치료제 설파살라진을 복용하는 궤양성대장염 환자는 엽산부족으로 심각한 빈혈을 유발할수 있음.
- 만성 엽산부족은 궤양성대장염 환자의 대장염 발병위험을 증가시킴.
3) 비타민 B6
- 궤양성 대장염 환자의 비타민 B6 평균혈장농도가 낮음.
- 비타민 B6는 호모시스테인과 관련하여 항혈전, 항응고작용이 있음. 부족하면 혈전에 의해 혈관이 막히는 혈전색전증이 일어날 수 있음.
4) 비타민 C
- 동물실험에서 비타민 C의 항산화효과는 궤양성대장염에 효과적
5) 비타민 D
- 궤양성대장염, 크론병과 같은 염증성 장염을 가진 150명의 환자들은 비타민 D의 평균혈청농도가 현저히 낮음.
- 궤양성 대장염 환자의 25%는 비타민 D부족으로 부갑상선기능항진증으로 진행함.
6) 마그네슘
- 설사로 인해 마그네슘이 소실되기 쉬운 궤양성대장염 환자는 마그네슘 부족이 흔함.
- 마그네슘이 부족해지면 심실성 빈맥이 나타날 수 있고 혼란, 불안, 몸떨림 등의 증상이 나타날 수 있음
- 가볍게는 피로, 근육경련, 두근거림, 두통 등
7) 철
- 궤양성대장염 환자의 36%가 철결핍성 빈혈이 발생함.
클릭클릭
8) DHEA
- DHEA는 루프스, 류마티스관절염, 피부근염 등 자가면역질환에 효과적
- 부작용이 있으므로 주의해서 사용
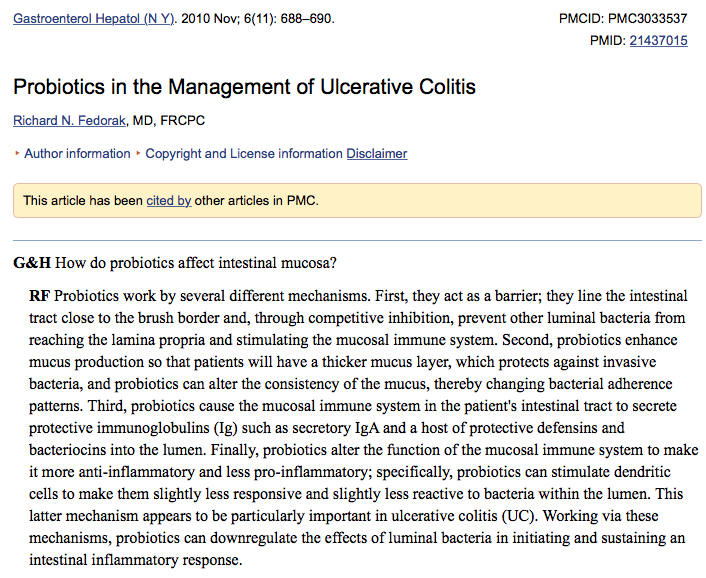
9) 프로바이오틱스(유산균, 유익균, 소장균-대장균)
- 1년이상 꾸준히 치료해야
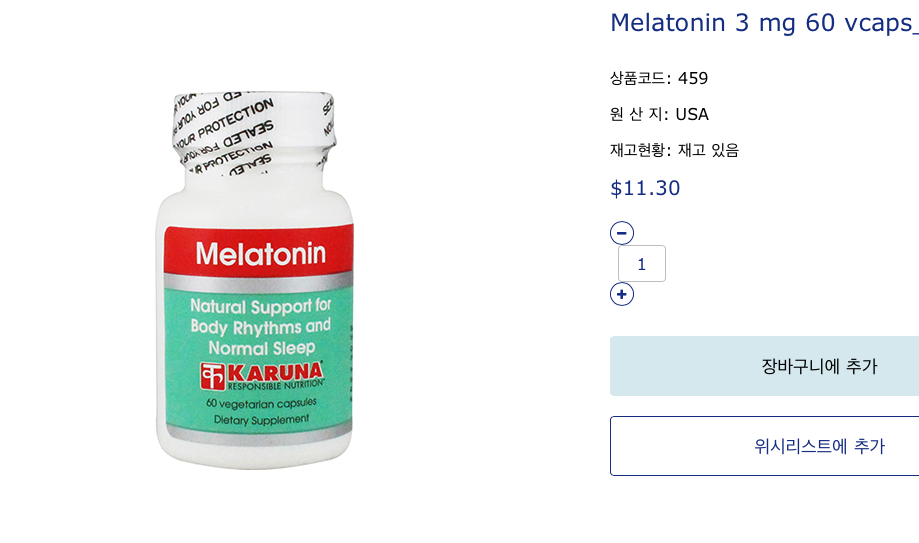
10) 멜라토닌
- 궤양성대장염에 멜라토닌 하루 3mg복용하면 효과적
11) 커큐민(curcumin)
- 커큐민을 매일 2g씩 6개월간 복용하면 궤양성대장염 재발율 감소
12) 브로멜레인
- 궤양성대장염에 효과적임.
궤양성 대장염은 6가지 영양물질이 부족해지므로 반드시 고려해야
- 칼륨
- 비타민 D
- 철분
- 비타민 B
- 포타슘
- 마그네슘
When you have ulcerative colitis (UC), you may not get enough of the nutrients your body needs. Problems with how your body absorbs nutrients, as well as blood loss, diarrhea, and even the drugs used to treat this inflammatory bowel disease all can increase the risk of nutritional deficiency. But maintaining healthy levels of essential nutrients is possible with proper nutrition and supplementation. Find out what nutritional deficiencies are most commonly associated with ulcerative colitis, and what you can do about it.
Calcium and Vitamin D Keep Bones Strong
Kristi L. King, MPH, RDN, senior pediatric dietitian at Texas Children's Hospital and a clinical instructor at the Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, said that low stores of calcium and vitamin D are the main vitamin and mineral deficiencies in patients with ulcerative colitis. When you have colitis, "the intestines and colon don’t absorb nutrients in the same way that they do for someone without the disease," she says, adding that many drugs commonly prescribed to treat colitis, such as prednisone, can also interfere with the absorption of calcium and vitamin D when used for prolonged periods of time.
You may not have any noticeable symptoms, but your gastroenterologist should regularly check for these deficiencies as part of ulcerative colitis treatment, King says. Over-the-counter supplements can help restore healthy levels. In serious cases, you may need very high doses at first, followed by a lower maintenance dose. Making some changes to your diet will help, too.
Dairy products are rich sources for both calcium and vitamin D, but according to a study published in October 2014 in the journal Food and Nutrition Sciences, many people with UC restrict dairy from their diets due to concerns that it will trigger symptoms. If you’re sensitive to dairy, grab a glass of soy or rice milk that’s fortified with calcium and Vitamin D instead. You can also increase your leafy green vegetables (cooked to minimize bowel irritation), which are rich in these nutrients.
Iron Helps Fight Fatigue
Iron deficiency occurs in roughly 60 to 80 percent of people with inflammatory bowel disease, affecting their quality of life, according to a review published in 2013 in the journal Annals of Gastroenterology. This deficiency may be due to blood loss from bloody diarrhea or internal ulcerations of the colon, or could be caused by some drugs used to treat ulcerative colitis, such as cholestyramine.
“Symptoms of iron deficiency include fatigue, pale skin, and a profound craving for ice or mud,” says David T. Rubin, MD, Joseph B. Kirsner professor of medicine and co-director of the Digestive Diseases Center at The University of Chicago Medical Center in Illinois.
Although it was a panacea for Popeye, Dr. Rubin says that spinach alone isn't enough to treat iron deficiency. Options include iron supplements, though they may make ulcerative colitis symptoms worse in some people, and intravenous iron infusions, which may also be used to replenish iron stores.
Only very rarely are blood transfusions used, Rubin says. Once your iron stores are back to normal, eating an iron-rich diet with foods like lean meats and cooked leafy greens can help keep you at a healthy level.
B Vitamins Can Boost Energy and Memory
People with ulcerative colitis may have problems absorbing folate — also known as folic acid or vitamin B9 — and other B vitamins, especially vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is absorbed in only one part of the small intestine, known as the ileum, right before it hits the colon, says King. Some medications, such as cholestyramine and sulfasalazine, can prevent B12 from being absorbed in this area and interfere with folate absorption, too.
Signs of a vitamin B deficiency are a lack of energy, balance issues, a pale tongue, and tingling in the fingers and toes. Severe cases may cause memory loss and disorientation. Once diagnosed by a blood test, folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies may be treated with supplements. But if you're on a medication that interferes with vitamin B12 absorption, the only way to make sure you're getting enough of the vitamin is by injection, King adds.
In conjunction with treatment, eat a diet rich in sources of B vitamins and folate, like meat, poultry, and eggs, to maintain healthy levels.
Potassium Helps Relieve Muscle Cramps
Potassium deficiency may be the result of chronic vomiting and diarrhea or from use of corticosteroids (prednisone). King says potassium deficiency comes into play with ulcerative colitis because the colon is the final place where it's absorbed in the body. “The colon actually reabsorbs potassium, and it goes through the bloodstream that way,” she says.
Symptoms of this deficiency may include muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, or feeling dizzy and fainting. Eating a diet high in potassium-rich foods, like bananas, cooked leafy green vegetables, and potatoes, is usually enough to correct a potassium deficiency, said King. Getting too much potassium through an over-the-counter supplement may increase the risk of heart problems.
Magnesium Can Reduce Diarrhea
Magnesium deficiency is also an issue for people with ulcerative colitis because the mineral is absorbed in the colon. Magnesium loss is also associated with chronic diarrhea.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency include muscle twitching, irritability, and poor memory.
To treat this deficiency, you may need to take oral supplements or eat more magnesium-rich foods that you can tolerate, such as creamy peanut butter, cocoa, and seafood. Other common magnesium-rich foods, like nuts and dried fruits, may not be as easily digested. "You want to make sure to talk to your registered dietitian or doctor because too much magnesium can cause diarrhea,” says King.