beyond reason
미량원소 치유의학의 세계
![]() The role of short- chain fatty acids in microbiota-gut-brain communication.pdf
The role of short- chain fatty acids in microbiota-gut-brain communication.pdf
인체의 소장, 대장에는 1.5kg이 넘는 혐기성, 호기성 세균들이 살고 있음.
그중 락토바실러스는 1/4을 차지하고 비피도박테리아, 대장균 등 100조개의 세균
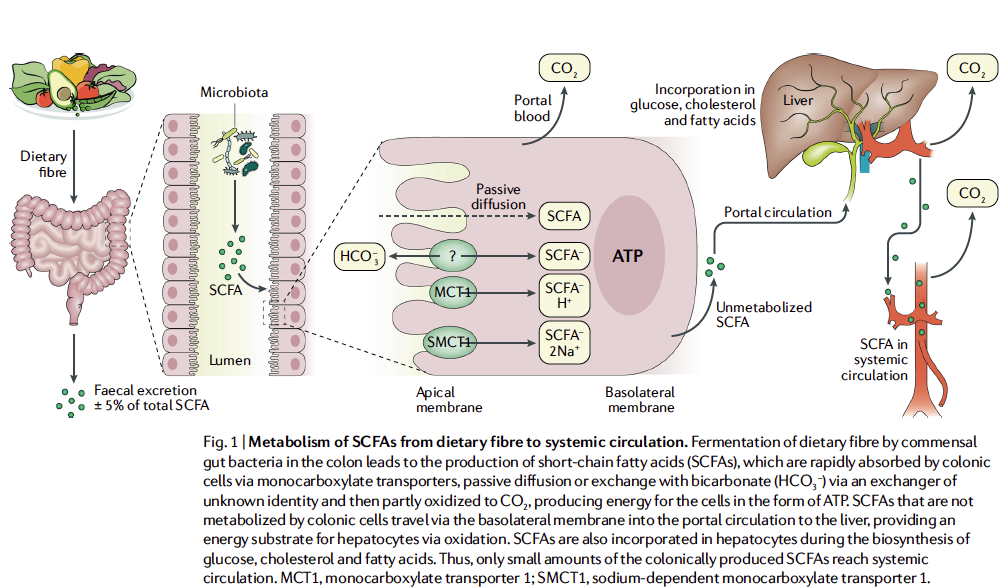
이들은 대사과정에서 SCFAs를 생성하여 보이지 않는 장기로서 기능을 함.
SCFAs에 대해서 알아보기!
Short- chain fatty acids (SCFAs), the main metabolites produced by bacterial fermentation of dietary fibre in the gastrointestinal tract, are speculated to have a key role in microbiota–gut–brain crosstalk. However, the pathways through which SCFAs might influence psychological functioning, including affective and cognitive processes and their neural basis, have not been fully elucidated. Furthermore, research directly exploring the role of SCFAs as potential mediators of the effects of microbiota- targeted interventions on affective and cognitive functioning is sparse, especially in humans.
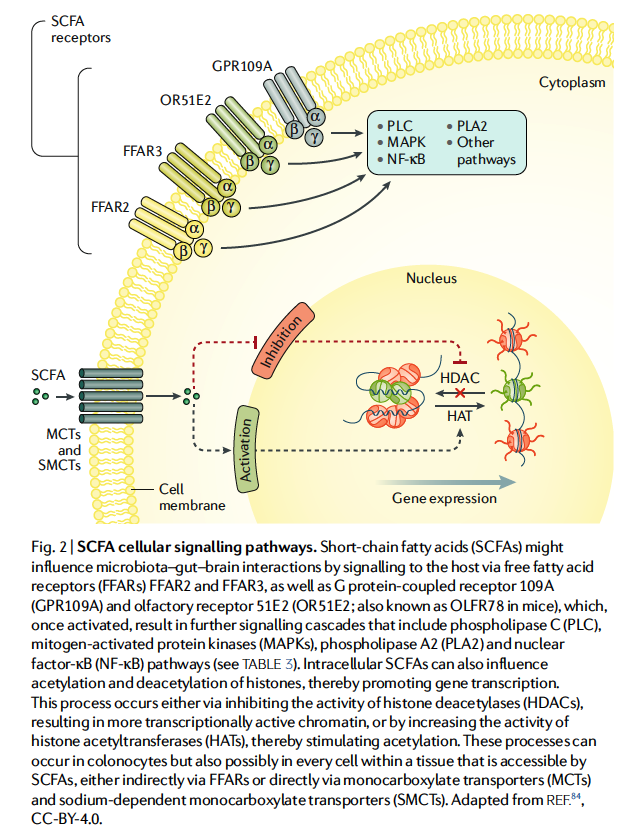
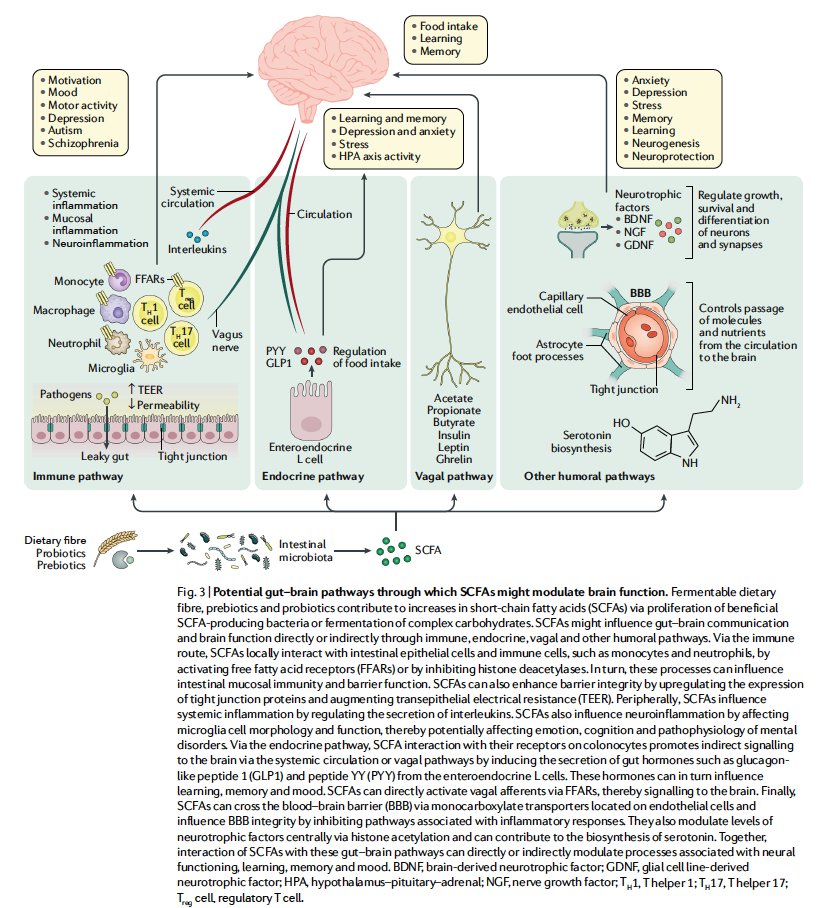
This Review summarizes existing knowledge on the potential of SCFAs to directly or indirectly mediate microbiota–gut–brain interactions. The effects of SCFAs on cellular systems and their interaction with gut–brain signalling pathways including immune, endocrine, neural and humoral routes are described. The effects of microbiota- targeted interventions such as prebiotics, probiotics and diet on psychological functioning and the putative mediating role of SCFA signalling will also be discussed, as well as the relationship between SCFAs and psychobiological processes. Finally , future directions to facilitate direct investigation of the effect of SCFAs on psychological functioning are outlined.