beyond reason
담즙산은 간에서 만들어지고
지방을 먹을때 분비됨
클릭클릭
A B S T R A C T
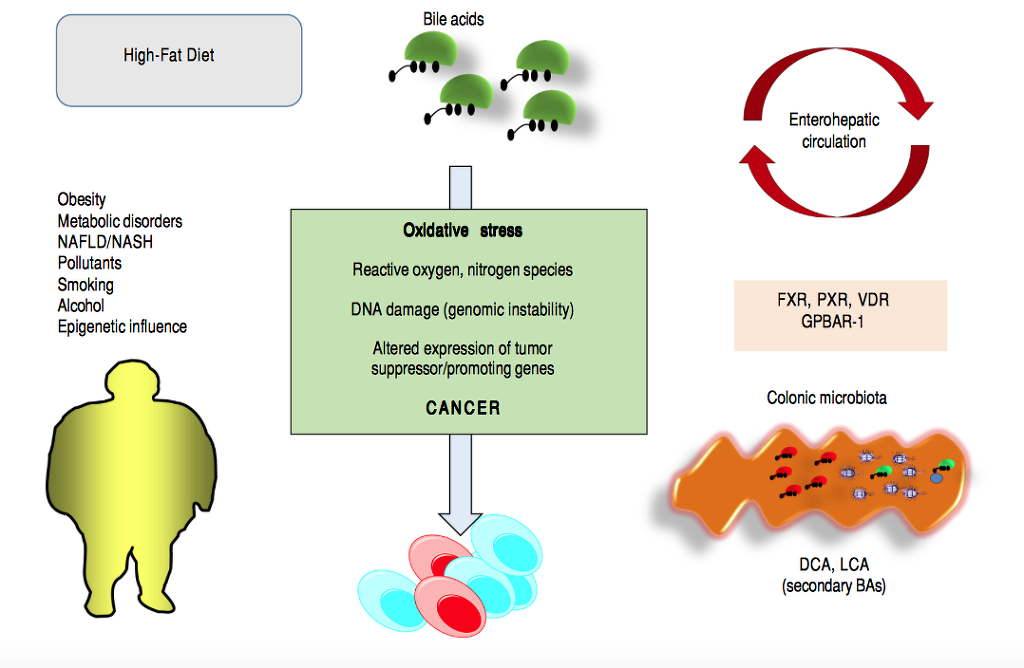
Bile acids (BAs) regulate the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, cholesterol and lipids but have also a key role as signaling molecules and in the modulation of epithelial cell proliferation, gene expression and metabolism. These homeostatic pathways, when disrupted, are able to promote local inflammation, systemic metabolic disorders and, ultimately, cancer. The effect of hydrophobic BAs, in particular, can be linked with cancer in several digestive (mainly oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, biliary tract, colon) and ex- tra-digestive organs (i.e. prostate, breast) through a complex series of mechanisms including direct oxidative stress with DNA dam- age, apoptosis, epigenetic factors regulating gene expression, reduced/increased expression of nuclear receptors (mainly farnesoid X receptor, FXR) and altered composition of gut microbiota, also acting as a common interface between environmental factors (includ- ing diet, lifestyle, exposure to toxics) and the molecular events promoting cancerogenesis. Primary prevention strategies (i.e. chang- es in dietary habits and lifestyle, reduced exposure to environmental toxics) mainly able to modulate gut microbiota and the epigenome, and the therapeutic use of hydrophilic BAs to counterbalance the negative effects of the more hydrophobic BAs might be, in the near future, part of useful tools for cancer prevention and management.
Key words. Bile acids. Cancer. Microbiota. FXR. Environment. Epigenome.