Re: Niacin Cures Systemic NAD+ Deficiency and Improves Muscle Performance i
작성자문형철작성시간20.09.29조회수201 목록 댓글 0beyond reason
Niacinamide (Vitamin B-3) is a form of Niacin, a water soluble B-Vitamin. It is a derivative of Niacin that does not cause the "flush" normally associated with taking high doses of Niacin. Niacinamide is readily converted into the bioactive forms of Niacin, NAD+, NADH, NADP, and NADPH, which are vital cofactors in cellular energy production and are critical for the maintenance of DNA stability.
- 나이아신아마이드는 나이아신의 한 형태이고 수용성 B비타민.
- 나이아신아마이드는 쉽게 나이아신, NAD+, NADH, NADP, NADPH의 생물학적 형태로 전환되어 세포에서 에너지를 생산하는데 중요한 보조인자(cofactor)로 작용하고 DNA stability의 유지에 중요한 역할을 함.



Highlights
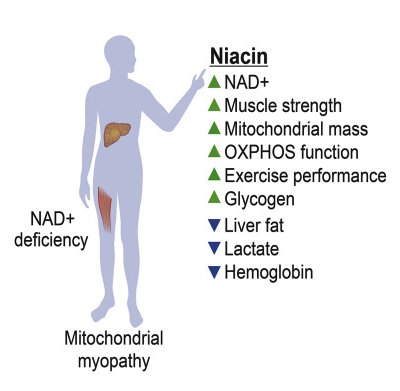
- Mitochondrial myopathy patients have NAD + deficiency in muscle and blood
- Niacin is an efficient NAD + booster in humans
- Niacin improves muscle strength and fatty liver in mitochondrial myopathy
- Niacin boosts muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and respiratory chain activity in humans
Summary
NAD + is a redox-active metabolite, the depletion of which has been proposed to promote aging and degenerative diseases in rodents. However, whether NAD + depletion occurs in patients with degenerative disorders and whether NAD + repletion improves their symptoms has remained open. Here, we report systemic NAD + deficiency in adult-onset mitochondrial myopathy patients.
We administered an increasing dose of NAD +-booster niacin, a vitamin B3 form (to 750–1,000 mg/day) for patients and their matched controls for 10 or 4 months, respectively. Blood NAD + increased in all subjects, up to 8-fold, and muscle NAD + of patients reached the level of their controls. Some patients showed anemia tendency, while muscle strength and mitochondrial biogenesis increased in all subjects. In patients, muscle metabolome shifted toward controls and liver fat decreased even 50%. Our evidence indicates that blood analysis is useful in identifying NAD + deficiency and points niacin to be an efficient NAD + booster for treating mitochondrial myopathy.