Middle mediastinum
Zane T.Hammoud and Micheal J.Liptay
1. Introduction
1) Mediastinum
: space that lies between two pleural cavity
: lies many vital structures
2) Mediastinum border
-superiorly : thoracic inlet
-inferiorly : thoracic surface of the diaphragm
-anteriorly : sternum
-inferiorly : spine
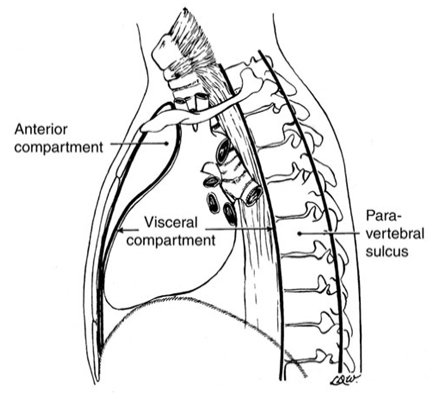
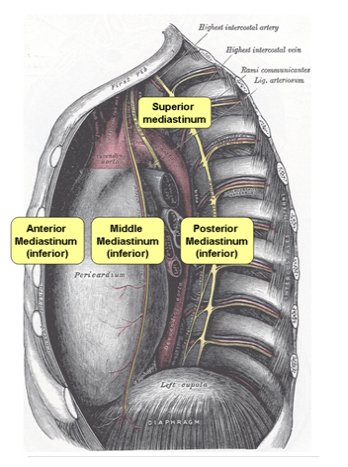
3) Mediastinum three imaginary compartments
: not truly a mediastinal space, but convenient to classify
① Anterior compartment
: space inferior to the innominate vein , posterior to the sternum
: anterior to the anterior surfaces of the pericardium and of the great vessels
② Middle (or visceral) compartment
: from anterior surfaces of the vertebral bodies to the posterior aspect of the
pericardium
③ Posterior compartment
:consists of the paravertebral sulci or costovertebral regions
2. Anatomy / Contents of middle mediastinum
1) Lymph node
: rich in lymphatics and in lymph node groups
: major lymph node group à drain the lungs and esophagus
: minor lymph node group à located on the diaphragmatic aspect of the pericardium
2) Trachea
: entire intrathoracic portion of the trachea
: proximal portions of the right and left mainstem brochi
3) Esophagus
: major portion of intrathoracic esophagus
4) Heart and great vessels
: heart, pericardium, ascending aorta, proximal aortic arch
3. Investigation and diagnosis
1) Noninvasive investigations
① Chest X-ray
- one of the most common noninvasive diagnostic investigative tools
- abnormality suspected on CXR lead to further investigation
: enlargement of the mediastinum suggestive of a mass
: narrowing of the trachea suggestive of stenosis
: prominence of the pulmonary hila suggestive of adenopathy
- abnormality of the heart or great vessels
: implied only by the location of mediastinal widening
② Computed tomography
- currently the most useful imaging modality
- high-resolution CT scan
: essential in the visualization of mediastinal structures
: addition of intravenous as well as oral contrast agents adds to the information
③ Other techniques
- Ultrasonography
: characterize a middle mediastinal mass
: rarely provides information not provided by CT
- MRI imaging
: useful in the evaluation of masses located in the posterior mediastinum
- Positron Emission tomography(PET) scanning
: useful in the noninvasive staging of the mediastinum in malignancies
: not anatomical scan
à precise location of any abnormality may be difficult to determine
∴ CT-PET scanning may overcome this limitation
2) Invasive procedure
- Percutaneous transthoracic FNB (fine needle biopsy)
어떤 치료를 할지 결정하기 전에 조직 진단이 필요하다면 percutaneous biopsy를 통해서 진단을 내릴 수 있다. 대개 percutaneous biopsy는 마취과 의사를 대동하고 필요에 따라 IV로 진정제를 주기도 하면서 초음파나 CT의 도움을 받으면서 행하여진다. middle mediastinal mass의 FNB는 CT를 보고 흉강을 통해 폐를 지나 할 수 있다. 거의 대부분의 경우에 있어서 성공적인 biopsy가 이루어지고 합병증 또한 거의 없다. 그러나 이 방법은 실패를 하였을 때 좀 더 침습적인 외과적 접근을 필요로 하게 된다. 이는 환자들이 2가지 이상의 시술을 받을 가능성이 있다는 것을 의미하기도 한다. (가격대비 비효과적이고 잠재적인 합병증 또한 생각을 해야 한다.) 위와 같은 이유로 우리는 매우 한정된 상황에서만 이 방법을 사용한다.
최근에는 sternum을 통한 core needle biopsy가 성공률이 좋고 이환율도 낮다는 보고가 있다.
middle mediastinum 에 있는 mass의 조직을 얻기 위해 cervical mediastinoscopy 가 이용 되기도 한다. 이 방법은 많이 커져있는 림프절이나 예전에 림프절이었을 것 같은 mass에 많이 이용된다. 특히나 mass가 유독 한쪽면에만 우세하게 위치하고 있는 몇몇 경우에는 조직을 얻기 위해서 anterior mediastinotomy가 이용될 수도 있다. 위의 방법들중 하나, 경우에 따라서는 두가지 방법을 동시에 사용하여 우리는 대부분의 케이스에서 진단을 내릴 수 있다.
표 41-1 benign mediastinal lymphadenopathy의 조직학적인 진단 (N=206)
|
diagnosis |
number (%) |
|
noncaseating granuloma (비건락육아종) |
130 (63%) |
|
follicular reactive hyperplasia |
20 (10%) |
|
caseating granuloma (건락육아종) |
16 (8%) |
|
anthracosis (석탄가루증) |
11 (5%) |
|
other |
29 (14%) |
표 41-2 확인된 nonbronchogenic cancer의 mediastinoscopy를 통한 병리학적인 진단 (N=161)
|
diagnosis |
number (%) |
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma (비호지킨 림프종) |
81 (50%) |
|
Hodgkin lymphoma (비호지킨 림프종) |
28 (17%) |
|
melanoma (악성 흑색종) |
10 (6%) |
|
sarcoma (육종) |
9 (6%) |
|
other |
33 (20%) |
VATS는 mediastinal mass들을 진단과 치료함에 있어서 많이 사용되고 있다. 이 방법은 mediastinum의 거의 모든 부분을 잘 보여줄뿐더러 외과의사들에게 좀 더 다양한 절개의 방법을 제공한다. 또한 해부학적으로도 주변 구조물과의 관계를 잘 보여주고 지금까지 해왔던 thoracostomy와 비교하여 외과적인 손상을 줄일 수도 있다. 절제하지 않은 mass나 benign cyst와 같은 benign mass의 절제는 VATS를 통해서 쉽게 할 수 있다. 이러한 이유들 때문에 VATS는 다양한 mediastinal lesion의 관리에 많이 사용되고 있고 그 추세 또한 증가중이다.
3) other technique
thoracostomy나 full sternotomy는 조직 진단에 거의 사용하지를 않는다. 그러나 이 방법은 특히나 mediastinal mass에는 사용할 수 있는 가능성이 있다. 몇몇 사람들은 mediastinal mass에 있어서 초음파를 통해서 내시경으로 FNAB (fine needle aspiration biopsy)를 하는 것이 진단을 내릴 수 있는 방법이라고 보고한다. bronchoscopy는 특히나 기도 질환응 평가를 내리는데 있어서는 도움이 된다. 반면에 esopagoscopy는 식도 질환의 병리학적인 평가를 내리는데 있어서 유용하다.
4. SPECIFIC DISEASE
1) Adenopathy
malignant mediastinal lymphadenopathy의 가장 흔한 원인은 폐암의 전이이다. hilar lymph node의 침범에 따라 양성과 악성을 결정할 수 있지만 이 문제는 실제 임상에서 어려운 문제이다. 원발성 폐암의 위치와 종류에 기초해서 보면 mediastinal 림프절은 어떤 stage에서건 포함되어 있다. 진행된 폐암에서 영상 의학적인 사진들을 보면 기도 주변의 림프절들이 커져 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
식도암이나 기관지 암 같은 경우에도 mediastinal 림프절에 전이를 시킬 수 있다. 흔하지는 않지만 다른 몸 기관의 암들도 mediastinal 림프절에 암을 전이 시킬 수 있다.
lymphoma (림프종)는 mediastinal tumor 중에 가장 흔한 것 중의 하나이다. 호지킨 림프종과 비호지킨 림프종은 mediastinal adenopathy의 형태로 나타난다. 비록 이것들이 anterior mediastinum에 있다고 하더라도 이것들은 mediastinum의 어떤 림프절에도 전반적으로 영향을 끼칠 수 있다.
광범위한 염증 반응 또한 mediastinal 림프절을 크게 할 수도 있다. sarcoidosis는 양성 mediastinal lymphadenopathy의 흔한 원인중 하나이다. 박테리아성 폐렴이나 바이러스성 폐렴, 간질 폐 질환, 비특이적인 염증성 폐 질환은 mediastinal lymphadenopathy를 일으킨다. histoplasmosis와 cryptococcosis와 같은 진균 감염 또한 mediastinal 림프절을 침범 할 수 있다. 특히 HIV 환자나 이식을 받은 환자에게서 잘 생긴다.
그 밖에 선천성 심부전이나 Castleman's disease, 거대 림프절 증식증 등이 mediastinal lymphadenopathy 의 원인이 되기도 한다.
2) Diseases of the trachea
성인 기관지 (방패연골부터 carina까지)의 길이는 보통 11cm 정도 된다. 기도의 대부분은 middle mediastinum에 위치를 한다. 양성과 악성 다양하게 기도를 침범할 수 있다. 인투베이션을 한 후나 tracheostomy를 하는 와중에 생긴 양성 종양에 의해서 기도는 눌릴 수 있게 되고 이로 인해서 wheezing이나 stridor이 들릴 수 있다. 영상학적으로 보면 기도 주변이 전체적으로 좁아져 있는 것을 확인 할 수 있다. 갑상선 암에 의해서 기도가 압박을 받게 되면 호흡기적인 증상과 의미있는 영상학적 진단이 나온다.
기도에서 잘 생길 수 있는 것은 squamous carcinoma와 adenoid cystic carcinoma이다. 이 둘은 거의 같은 빈도로 일어난다. 이것들로 인해서 호흡기적인 증상과 객혈과 같은 것들이 일어난다. 거의 모든 기도 질환들이 영상학적으로 보일 수 있지만 기관지 내시경을 통한 평가는 거의 모든 경우에서 필수이다.
3) Diseases of Esophagus
해부학적 위치 : begins in the neck at the level of the cricopharyngeus muscle
ends at the gastroesophageal junction
① esophageal mass
- Leiomyoma
: most common benign esophageal tumor
extraluminal esophageal mass
treatment - simple enucleation of the tumor
- Malignant lesions
: squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma
advanced stage에서 mediasternum의 구조를 compression
② Tracheoesophageal fistulas
: secondary to malignancy
보통 recurrent pneumonias와 함께 나타남.
③ Perforation
: mediastinitis를 일으키는 흔한 원인
-증상 : 진단까지의 시간에 따라 asymptomatic or critically ill
-영상 : presence of air in the mediastinum 시 의심
④ Mediastinitis
: 영상 - diffuse inflammation( 정상 지방층 소실과 함께), occasion, gas bubbles
4) Cysts
: 어린이와 성인에서 호발
① Foregut cysts
: 특징 - spheric, thin wall
: 증상 - dyspnea, dysphagia, pain
- Bronchogenic cyst
: 특징 - unilocular, ciliated columnar epithelium
: 호발부위 - carina
: 증상 - 무증상
airway compression이나 cyst 내 infection으로 인한 증상 있을 수 있음.
: 치료 - complete surgical excision
최근 VATS를 이용한 접근이 좋은 결과를 보이고 있음.
- Esophageal cyst
: 특징 - embedded entirely within the esophageal wall
: 증상 - pain and/or dysphagia
: 치료 - surgical excision, thoracoscopic resection
- Pleuropericardial cysts
: 호발 부위 - right cardiophrenic angle
: 증상 - dyspnea, chest pain
: 치료 - Radiology-guided needle aspiration, thoracoscopic surgical resection
5) Mediastinal infection
: secondary to esophageal perforation or to postoperative sternal infections after
sternotomy
- perforation
: surgical emergency
치료 - surgical debridement + primary repair
② Postoperative sternal infections
치료 - aggressive surgical debridement, + early muscle flap closure
③ Descending necrotizing mediastinitis
: from odontogenic abscess
치료 - systemic antibiotics, surgical drainage, tracheostomy
Chronic fibrosing mediastinitis
: by chronic fungal infections
치료 - relief of symptoms